Development of an imaging-guided CEA-pretargeted radionuclide treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: first clinical results
- PMID: 23860529
- PMCID: PMC3749562
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.376
Development of an imaging-guided CEA-pretargeted radionuclide treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: first clinical results
Abstract
Background: Radiolabelled antibody targeting of cancer is limited by slow blood clearance. Pretargeting with a non-radiolabelled bispecific monoclonal antibody (bsMAb) followed by a rapidly clearing radiolabelled hapten peptide improves tumour localisation. The primary goals of this first pretargeting study in patients with the anti-CEACAM5 × anti-hapten (HSG) bsMAb, TF2, and the radiolabelled hapten-peptide, IMP288, were to assess optimal pretargeting conditions and safety in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC).
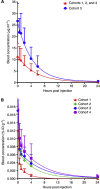
Methods: Different dose schedules were studied in four cohorts of five patients: (1) shortening the interval between the bsMAb and peptide administration (5 days vs 1 day), (2) escalating the TF2 dose (from 75 to 150 mg), and (3) reducing the peptide dose (from 100 to 25 μg). After confirmation of tumour targeting by (111)In-IMP288, patients were treated with a bsMAb/(177)Lu-IMP288 cycle.
Results: Rapid and selective tumour targeting of the radiolabelled peptide was visualised within 1 h, with high tumour-to-tissue ratios (>20 at 24 h). Improved tumour targeting was achieved with a 1-day interval between the administration of the bsMAb and the peptide and with the 25-μg peptide dose. High (177)Lu-IMP288 doses (2.5-7.4 GBq) were well tolerated, with some manageable TF2 infusion reactions, and transient grades 3-4 thrombocytopaenia in 10% of the patients who received (177)Lu-IMP288.
Conclusion: This phase I study demonstrates for the first time that pretargeting with bsMAb TF2 and radiolabelled IMP288 in patients with CEA-expressing CRC is feasible and safe. With this pretargeting method, tumours are specifically and rapidly targeted.
Figures



References
-
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26 (10:1626–1634. - PubMed
-
- Boerman OC, van Schaijk FG, Oyen WJ, Corstens FH. Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy of cancer: progress step by step. J Nucl Med. 2003;44 (3:400–411. - PubMed
-
- Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A, Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de Braud F, Donea S, Ludwig H, Schuch G, Stroh C, Loos AH, Zubel A, Koralewski P. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27 (5:663–671. - PubMed
-
- Chang CH, Sharkey RM, Rossi EA, Karacay H, McBride W, Hansen HJ, Chatal JF, Barbet J, Goldenberg DM. Molecular advances in pretargeting radioimunotherapy with bispecific antibodies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1 (7:553–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

