Fluphenazine (oral) versus placebo for schizophrenia
- PMID: 23861067
- PMCID: PMC3997140
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006352.pub2
Fluphenazine (oral) versus placebo for schizophrenia
Update in
-
Fluphenazine (oral) versus placebo for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 12;6(6):CD006352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006352.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29893410 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Fluphenazine is one of the first drugs to be classed as an 'antipsychotic' and has been widely available for five decades.
Objectives: To compare the effects of oral fluphenazine with placebo for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Search methods: We updated searches of the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's trials register, which includes relevant randomised controlled trials from the bibliographic databases Biological Abstracts, CINAHL, The Central Register of Controlled Trials in The Cochrane Library, EMBASE, MEDLINE, PsycLIT, LILACS, PSYNDEX, Sociological Abstracts and Sociofile, 15 May, 2012. References of all identified studies were searched for further trial citations.
Selection criteria: We sought all randomised controlled trials comparing oral fluphenazine with placebo relevant to people with schizophrenia. Primary outcomes of interest were global state and adverse effects.
Data collection and analysis: We inspected citations and abstracts independently, ordered papers and re-inspected and quality assessed trials. We extracted data independently. Dichotomous data were analysed using fixed-effect risk ratio (RR) and the 95% confidence interval (CI). Continuous data were excluded if more than 50% of people were lost to follow-up, but, where possible, mean differences (MD) were calculated.
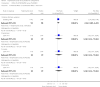
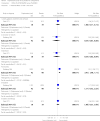
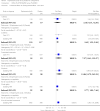
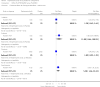
Main results: From over 1200 electronic records of 415 studies identified by our initial search and this updated search, we excluded 48 potentially relevant studies and included seven trials published between 1964 and 1999 that randomised 439 (mostly adult participants). No new included trials were identified for this review update. Compared with placebo, global state outcomes of 'not improved or worsened' were not significantly different in the medium term in one small study (n = 50, 1 RCT, RR 1.12 CI 0.79 to 1.58, very low quality of evidence). The risk of relapse in the long term was greater in two small studies in people receiving placebo (n = 86, 2 RCTs, RR 0.39 CI 0.05 to 3.31, very low quality of evidence), however with high degree of heterogeneity in the results. Only one person allocated fluphenazine was reported in the same small study to have died on long-term follow-up (n = 50, 1 RCT, RR 2.38 CI 0.10 to 55.72, low quality of evidence). Short-term extrapyramidal adverse effects were significantly more frequent with fluphenazine compared to placebo in two other studies for the outcomes of akathisia (n = 227, 2 RCTs, RR 3.43 CI 1.23 to 9.56, moderate quality of evidence) and rigidity (n = 227, 2 RCTs, RR 3.54 CI 1.76 to 7.14, moderate quality of evidence).
Authors' conclusions: The findings in this review confirm much that clinicians and recipients of care already know, but they provide quantification to support clinical impression. Fluphenazine's global position as an effective treatment for psychoses is not threatened by the outcome of this review. However, fluphenazine is an imperfect treatment and if accessible, other inexpensive drugs less associated with adverse effects may be an equally effective choice for people with schizophrenia.
Figures


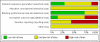




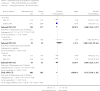
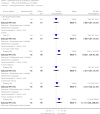


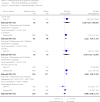









Update of
-
Oral fluphenazine versus placebo for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD006352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006352. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 17;(7):CD006352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006352.pub2. PMID: 17253589 Updated.
References
-
- Carpenter WT, Jr, Buchanan RW, Kirkpatrick B, Breier AF. Diazepam treatment of early signs of exacerbation in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry. 1999;156(2):299–303. [MEDLINE: 99178642] - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Charalampous KD, Serafetinides EA, Trousdale W, Colmore JP. Drug treatment in newly admitted schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1971;25(5):404–9. [MEDLINE: 72081786] - PubMed
-
- Cole JO, Goldberg SC, Klerman GL. Phenothiazine treatment in acute schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1964;10:246–61. [MEDLINE: 71204770] - PubMed
-
- Gibbons RD, Lewine RRJ, Davis JM, Schooler NR, Cole JO. An empirical test of a kraepelinian vs. a bleulerian view of negative symptoms. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 1985;11(3):390–5. [MEDLINE: 71204770] - PubMed
-
- Goldberg SC, Klerman GL, Cole JO. Changes in schizophrenic psychopathology and ward behaviour as a function of phenothiazine treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1965;111:120–33. [MEDLINE: 5677325] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

