AZD3514: a small molecule that modulates androgen receptor signaling and function in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23861347
- PMCID: PMC3769207
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1174
AZD3514: a small molecule that modulates androgen receptor signaling and function in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
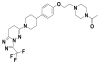
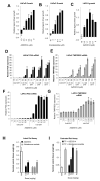
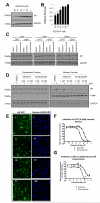
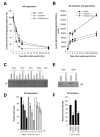
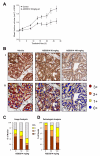
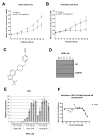
Continued androgen receptor (AR) expression and signaling is a key driver in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after classical androgen ablation therapies have failed, and therefore remains a target for the treatment of progressive disease. Here, we describe the biological characterization of AZD3514, an orally bioavailable drug that inhibits androgen-dependent and -independent AR signaling. AZD3514 modulates AR signaling through two distinct mechanisms, an inhibition of ligand-driven nuclear translocation of AR and a downregulation of receptor levels, both of which were observed in vitro and in vivo. AZD3514 inhibited testosterone-driven seminal vesicle development in juvenile male rats and the growth of androgen-dependent Dunning R3327H prostate tumors in adult rats. Furthermore, this class of compound showed antitumor activity in the HID28 mouse model of CRPC in vivo. AZD3514 is currently in phase I clinical evaluation.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer I the effect of castration, of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. CA Cancer J Clin. 1972;22:232–40. - PubMed
-
- Scher HI, Sawyers CL. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: Directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8253–61. - PubMed
-
- Attard G, Cooper CS, de Bono JS. Steroid hormone receptors in prostate cancer: A hard habit to break? Cancer Cell. 2009;16:458–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

