Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant
- PMID: 23861390
- PMCID: PMC3772193
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R113.472936
Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant
Abstract
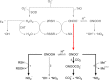
Peroxynitrite is the product of the diffusion-controlled reaction of nitric oxide and superoxide radicals. Peroxynitrite, a reactive short-lived peroxide with a pKa of 6.8, is a good oxidant and nucleophile. It also yields secondary free radical intermediates such as nitrogen dioxide and carbonate radicals. Much of nitric oxide- and superoxide-dependent cytotoxicity resides on peroxynitrite, which affects mitochondrial function and triggers cell death via oxidation and nitration reactions. Peroxynitrite is an endogenous toxicant but is also a cytotoxic effector against invading pathogens. The biological chemistry of peroxynitrite is modulated by endogenous antioxidant mechanisms and neutralized by synthetic compounds with peroxynitrite-scavenging capacity.
Keywords: Free Radicals; Nitric Oxide; Oxidative Stress; Peroxynitrite; Superoxide Dismutase (SOD); Superoxide Ion; Tyrosine Nitration.
Figures
References
-
- Ross W. G. M., Helman W. P., Buxton G. V., Huie R. E., Neta P. (1995) NDRL/NIST Solution Kinetics Database, Version 3.0, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD
-
- Fridovich I. (1995) Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64, 97–112 - PubMed
-
- Sies H., Jones D. P. (2007) Oxidative stress. in Encyclopedia of Stress (Fink G., ed) 2nd Ed., Vol. 3, pp. 45–48, Elsevier/Academic Press, London
-
- Gryglewski R. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. (1986) Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature 320, 454–456 - PubMed
-
- Ignarro L. J., Byrns R. E., Buga G. M., Wood K. S., Chaudhuri G. (1988) Pharmacological evidence that endothelium-derived relaxing factor is nitric oxide: use of pyrogallol and superoxide dismutase to study endothelium-dependent and nitric oxide-elicited vascular smooth muscle relaxation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 244, 181–189 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

