Integration of Different "-omics" Technologies Identifies Inhibition of the IGF1R-Akt-mTOR Signaling Cascade Involved in the Cytotoxic Effect of Shikonin against Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 23861714
- PMCID: PMC3703888
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/818709
Integration of Different "-omics" Technologies Identifies Inhibition of the IGF1R-Akt-mTOR Signaling Cascade Involved in the Cytotoxic Effect of Shikonin against Leukemia Cells
Abstract
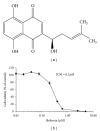
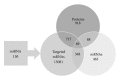
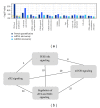
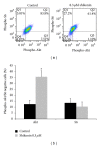
Hematological malignancies frequently have a poor prognosis and often remain incurable. Drug resistance, severe side effects, and relapse are major problems of currently used drugs, and new candidate compounds are required for improvement of therapy success. The naphthoquinone shikonin derived from the Chinese medicinal herb, Lithospermum erythrorhizon, is a promising candidate for the next generation of chemotherapy. The basal cellular mechanism of shikonin is the direct targeting of mitochondria. Cytotoxicity screenings showed that the compound is particularly effective against leukemia cells suggesting an additional cellular mechanism. mRNA and miRNA microarrays were used to analyze changes in gene expression in leukemia cells after shikonin treatment and combined with stable-isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. The integration of bioinformatics and the three "-omics" assays showed that the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway was affected by shikonin. Deregulations of this pathway are frequently associated with cancerogenesis, especially in a wide range of hematological malignancies. The effect on the PI3K-Akt-mTOR axis was validated by demonstrating a decreased phosphorylation of Akt and a direct inhibition of the IGF1R kinase activity after shikonin treatment. Our results indicate that inhibiting the IGF1R-Akt-mTOR signaling cascade is a new cellular mechanism of shikonin strengthening its potential for the treatment of hematological malignancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-tumor activity of Shikonin against afatinib resistant non-small cell lung cancer via negative regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2018 Dec 11;38(6):BSR20181693. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181693. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30420490 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of anilide (dicarboxylic acid) shikonin esters as antitumor agents through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Jun;111:104872. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104872. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33838560
-
Inhibition of c-MYC with involvement of ERK/JNK/MAPK and AKT pathways as a novel mechanism for shikonin and its derivatives in killing leukemia cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 17;6(36):38934-51. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5380. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26472107 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin, a naphthalene ingredient: Therapeutic actions, pharmacokinetics, toxicology, clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jan;94:153805. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153805. Epub 2021 Oct 24. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 34749177 Review.
-
Pharmacological properties and derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Nov;149:104463. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104463. Epub 2019 Sep 22. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31553936 Review.
Cited by
-
The anti-leukemia activity and mechanisms of shikonin: a mini review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 2;14:1271252. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1271252. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38026987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sho-saiko-to, a traditional herbal medicine, regulates gene expression and biological function by way of microRNAs in primary mouse hepatocytes.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 11;14:14. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-14. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24410935 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin changes the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inflammation-related genes in macrophages.J Nat Med. 2017 Oct;71(4):723-734. doi: 10.1007/s11418-017-1106-5. Epub 2017 Jul 11. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28699129
-
Network Pharmacology of Adaptogens in the Assessment of Their Pleiotropic Therapeutic Activity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;15(9):1051. doi: 10.3390/ph15091051. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of cellular and molecular factors determining the response of cancer cells to six ergot alkaloids.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Feb;33(1):32-44. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0168-4. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25342140
References
-
- Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Ab1 tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Ab1 positive cells. Nature Medicine. 1996;2(5):561–566. - PubMed
-
- Maloney DG, Grillo-López AJ, White CA, et al. IDEC-C2B8 (rituximab) anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with relapsed low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood. 1997;90(6):2188–2195. - PubMed
-
- Bertolini F. Lenalidomide for multiple myeloma. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367:573–575. - PubMed
-
- Norde WJ, Hobo W, van der Voort R, Dolstra H. Coinhibitory molecules in hematologic malignancies: targets for therapeutic intervention. Blood. 2012;120:728–736. - PubMed
-
- Martelli AM, Chiarini F, Evangelisti C, et al. Targeting the liver kinase B1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway as a therapeutic strategy for hematological malignancies. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets. 2012;16:729–742. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

