Recognition of accented and unaccented speech in different maskers by younger and older listeners
- PMID: 23862836
- PMCID: PMC3724774
- DOI: 10.1121/1.4807817
Recognition of accented and unaccented speech in different maskers by younger and older listeners
Abstract
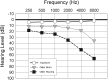
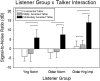
This investigation examined the effect of accent of target talkers and background speech maskers on listeners' ability to use cues to separate speech from noise. Differences in accent may create a disparity in the relative timing between signal and background, and such timing cues may be used to separate the target talker from the background speech masker. However, the use of this cue could be reduced for older listeners with temporal processing deficits, especially those with hearing loss. Participants were younger and older listeners with normal hearing and older listeners with hearing loss. Stimuli were IEEE sentences recorded in English by male native speakers of English and Spanish. These sentences were presented in different maskers that included speech-modulated noise and background babbles varying in talker gender and accent. Signal-to-noise ratios corresponding to 50% correct performance were measured. Results indicate that a pronounced Spanish accent limits a listener's ability to take advantage of cues to speech segregation and that a difference in accentedness between the target talker and background masker may be a useful cue for speech segregation. Older hearing-impaired listeners performed poorly in all conditions with the accented talkers.
Figures



References
-
- ANSI (2010). S3.6-2010, American National Standard Specification for Audiometers (Revision of ANSI S3.6-1996, 2004) (American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
-
- ANSI (1997). S3.5-1997, American National Standard Methods for Calculation of the Speech Intelligibility Index (Revision of ANSI S3.5-1969, R1986) (American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

