Cortical stimulation consolidates and reactivates visual experience: neural plasticity from magnetic entrainment of visual activity
- PMID: 23863977
- PMCID: PMC3714647
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02228
Cortical stimulation consolidates and reactivates visual experience: neural plasticity from magnetic entrainment of visual activity
Abstract
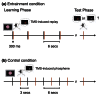
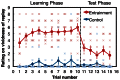
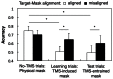
Delivering transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) shortly after the end of a visual stimulus can cause a TMS-induced 'replay' or 'visual echo' of the visual percept. In the current study, we find an entrainment effect that after repeated elicitations of TMS-induced replay with the same visual stimulus, the replay can be induced by TMS alone, without the need for the physical visual stimulus. In Experiment 1, we used a subjective rating task to examine the phenomenal aspects of TMS-entrained replays. In Experiment 2, we used an objective masking paradigm to quantitatively validate the phenomenon and to examine the involvement of low-level mechanisms. Results showed that the TMS-entrained replay was not only phenomenally experienced (Exp.1), but also able to hamper letter identification (Exp.2). The findings have implications in several directions: (1) the visual cortical representation and iconic memory, (2) experience-based plasticity in the visual cortex, and (3) their relationship to visual awareness.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The temporal dynamics of early visual cortex involvement in behavioral priming.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048808. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23155408 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity revealed by transcranial magnetic stimulation of early visual cortex.Neuroreport. 2000 May 15;11(7):1565-9. Neuroreport. 2000. PMID: 10841378
-
Occipital transcranial magnetic stimulation has opposing effects on visual and auditory stimulus detection: implications for multisensory interactions.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 24;27(43):11465-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2827-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17959789 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial magnetic stimulation of visual cortex in memory: cortical state, interference and reactivation of visual content in memory.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Jan 1;236(1):67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 22921373 Review.
-
Transcranial magnetic stimulation and vision.Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;116:655-69. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53497-2.00052-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24112931 Review.
Cited by
-
One-Shot Tagging During Wake and Cueing During Sleep With Spatiotemporal Patterns of Transcranial Electrical Stimulation Can Boost Long-Term Metamemory of Individual Episodes in Humans.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jan 10;13:1416. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01416. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31998067 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging deep learning to control neural oscillators.Biol Cybern. 2021 Jun;115(3):219-235. doi: 10.1007/s00422-021-00874-w. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Biol Cybern. 2021. PMID: 33909165
References
-
- Walsh V. & Pascual-Leone A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: A neurochronometrics of mind. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. (2005).
-
- Meyer B. U., Diehl R., Steinmetz H., Britton T. C. & Benecke R. Magnetic stimuli applied over motor and visual-cortex: Influence of coil position and field polarity on motor-responses, phosphenes, and eye-movements. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 43, 121–134 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Silvanto J., Muggleton N. G., Cowey A. & Walsh V. Neural adaptation reveals state-dependent effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 25, 1874–1881 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Silvanto J., Muggleton N. & Walsh V. State-dependency in brain stimulation studies of perception and cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 12, 447–54 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Wu D. A., Kamitani Y., Maeda F. & Shimojo S. Interaction of TMS-induced phosphenes and visual stimuli. J. Vis. 1(3), 198 (2001).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

