Identification of a KIR antisense lncRNA expressed by progenitor cells
- PMID: 23863987
- PMCID: PMC3808466
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2013.36
Identification of a KIR antisense lncRNA expressed by progenitor cells
Abstract
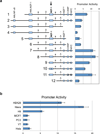
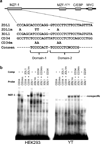
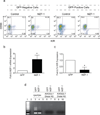
Human NK cells express cell surface class I MHC receptors (killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, KIR) in a probabilistic manner. Previous studies have shown that a distal promoter acts in conjunction with a proximal bidirectional promoter to control the selective activation of KIR genes. We report here the presence of an intron 2 promoter in several KIR genes that produce a spliced antisense transcript. This long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) transcript contains antisense sequence complementary to KIR-coding exons 1 and 2 as well as the proximal promoter region of the KIR genes. The antisense promoter contains myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF-1)-binding sites, a transcription factor found in hematopoietic progenitors and myeloid precursors. The KIR antisense lncRNA was detected only in progenitor cells or pluripotent cell lines, suggesting a function that is specific for stem cells. Overexpression of MZF-1 in developing NK cells led to decreased KIR expression, consistent with a role for the KIR antisense lncRNA in silencing KIR gene expression early in development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Carrington M, Norman P. The KIR Gene Cluster. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US), NCBI; 2001.
-
- Anderson SK, Ortaldo JR, McVicar DW. The ever-expanding Ly49 gene family: repertoire and signaling. Immunol Rev. 2001;181:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Parham P. MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:201–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

