Comparison study of intensity modulated arc therapy using single or multiple arcs to intensity modulated radiation therapy for high-risk prostate cancer
- PMID: 23865007
- PMCID: PMC3712173
- DOI: 10.3857/roj.2013.31.2.104
Comparison study of intensity modulated arc therapy using single or multiple arcs to intensity modulated radiation therapy for high-risk prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Intensity modulated arc therapy (IMAT) is a form of intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) that delivers dose in single or multiple arcs. We compared IMRT plans versus single-arc field (1ARC) and multi-arc fields (3ARC) IMAT plans in high-risk prostate cancer.
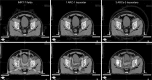
Materials and methods: Sixteen patients were studied. Prostate (PTV P ), right pelvic (PTV RtLN ) and left pelvic lymph nodes (PTV LtLN ), and organs at risk were contoured. PTV P , PTV RtLN , and PTV LtLN received 50.40 Gy followed by a boost to PTV B of 28.80 Gy. Three plans were per patient generated: IMRT, 1ARC, and 3ARC. We recorded the dose to the PTV, the mean dose (D MEAN ) to the organs at risk, and volume covered by the 50% isodose. Efficiency was evaluated by monitor units (MU) and beam on time (BOT). Conformity index (CI), Paddick gradient index, and homogeneity index (HI) were also calculated.
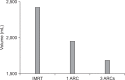
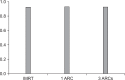
Results: Average Radiation Therapy Oncology Group CI was 1.17, 1.20, and 1.15 for IMRT, 1ARC, and 3ARC, respectively. The plans' HI were within 1% of each other. The D MEAN of bladder was within 2% of each other. The rectum D MEAN in IMRT plans was 10% lower dose than the arc plans (p < 0.0001). The GI of the 3ARC was superior to IMRT by 27.4% (p = 0.006). The average MU was highest in the IMRT plans (1686) versus 1ARC (575) versus 3ARC (1079). The average BOT was 6 minutes for IMRT compared to 1.3 and 2.9 for 1ARC and 3ARC IMAT (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: For high-risk prostate cancer, IMAT may offer a favorable dose gradient profile, conformity, MU and BOT compared to IMRT.
Keywords: High risk prostate cancer; Intensity modulated arc therapy; Intensity modulated radiation therapy; RapidArc.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




References
-
- Viani GA, Stefano EJ, Afonso SL. Higher-than-conventional radiation doses in localized prostate cancer treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:1405–1418. - PubMed
-
- Lawton CA, DeSilvio M, Roach M, 3rd, et al. An update of the phase III trial comparing whole pelvic to prostate only radiotherapy and neoadjuvant to adjuvant total androgen suppression: updated analysis of RTOG 94-13, with emphasis on unexpected hormone/radiation interactions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69:646–655. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Happersett L, et al. Clinical experience with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2000;55:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. RTOG Clinical Trials [Internet] Philadelphia, PA: RTOG; c2013. [cited 2013 May 23]. Available from: http://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable.aspx.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials