Consistency of effect of ezetimibe/simvastatin compared with intensified lipid-lowering treatment strategies in obese and non-obese diabetic subjects
- PMID: 23866306
- PMCID: PMC3722050
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-103
Consistency of effect of ezetimibe/simvastatin compared with intensified lipid-lowering treatment strategies in obese and non-obese diabetic subjects
Abstract
Purpose: This post hoc analysis assessed switching to ezetimibe/simvastatin 10/20 mg vs doubling the baseline statin dose to simvastatin 40 mg or atorvastatin 20 mg or switching to rosuvastatin 10 mg in subgroups of obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) and non-obese (BMI <30 kg/m2) diabetic subjects.
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, 12-week study of adults 18-79 years with cardiovascular disease with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥70 and ≤160 mg/dl. Percent change in LDL-C and other lipids was estimated.
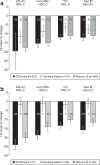
Results: In obese subjects (n = 466), percent changes in LDL-C and most other lipids were greater with ezetimibe/simvastatin vs doubling the baseline statin dose or switching to rosuvastatin. In non-obese subjects (n = 342), percent changes in LDL-C, total cholesterol, non-HDL-C, Apo B and Apo A-I were greater with ezetimibe/simvastatin vs doubling the baseline statin dose or switching to rosuvastatin; and treatment with ezetimibe/simvastatin resulted in greater changes in triglycerides vs rosuvastatin and HDL-C vs doubling the baseline statin dose. The safety profiles were generally similar.
Conclusions: Regardless of baseline obesity status, switching to ezetimibe/simvastatin was more effective at reducing LDL-C, total cholesterol, non-HDL-C, and Apo B vs doubling the baseline statin dose to simvastatin 40 mg or atorvastatin 20 mg or switching to rosuvastatin 10 mg.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00862251.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of ezetimibe/simvastatin combination compared with intensified lipid-lowering treatment strategies in diabetic subjects with and without metabolic syndrome.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Jun;15(6):513-22. doi: 10.1111/dom.12059. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013. PMID: 23279632 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in LDL-C levels and goal attainment associated with addition of ezetimibe to simvastatin, atorvastatin, or rosuvastatin compared with titrating statin monotherapy.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013;9:719-27. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S49840. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013. PMID: 24265554 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of efficacy and safety of an ezetimibe/simvastatin combination compared with other intensified lipid-lowering treatment strategies in diabetic patients with symptomatic cardiovascular disease.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013 May;10(3):277-86. doi: 10.1177/1479164112465212. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013. PMID: 23288881 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction after switching patients on other statins to rosuvastatin or simvastatin in a real-world clinical practice setting.Am J Manag Care. 2007 Dec;13 Suppl 10:S270-5. Am J Manag Care. 2007. PMID: 18095777 Review.
-
Is atorvastatin superior to other statins? Analysis of the clinical trials with atorvastatin having cardiovascular endpoints.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006 May;1(2):143-53. doi: 10.2174/157488706776876508. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006. PMID: 18473965 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Statin-Ezetimibe Combination Therapy with Statin Monotherapy in Patients with Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022 Jul;22(4):395-406. doi: 10.1007/s40256-021-00516-3. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34927215
-
Achievement of specified lipid and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels with two statins in Chinese patients with hypercholesterolaemia.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Sep 13;14:107. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0116-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26365713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons LA, Simons J. Diabetes and coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1714–1715. - PubMed
-
- Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: executive summary. Expert Panel on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight in Adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;68:899–917. - PubMed
-
- Expert panel on detection evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Genest J, McPherson R, Frohlich J, Anderson T, Campbell N, Carpentier A, Couture P, Dufour R, Fodor G, Francis GA, Grover S, Gupta M, Hegele RA, Lau DC, Leiter L, Lewis GF, Lonn E, Mancini GB, Ng D, Pearson GJ, Sniderman A, Stone JA, Ur E. Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease in the adult - 2009 recommendations. Can J Cardiol. 2009;2009(25):567–579. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

