Efficacy and safety of concentration-controlled everolimus with reduced-dose cyclosporine in Japanese de novo renal transplant patients: 12-month results
- PMID: 23866828
- PMCID: PMC3718642
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-1440-2-14
Efficacy and safety of concentration-controlled everolimus with reduced-dose cyclosporine in Japanese de novo renal transplant patients: 12-month results
Abstract
Background: No study to date has evaluated the efficacy and safety of everolimus with reduced-exposure cyclosporine in Japanese de-novo renal transplant (RTx) patients.
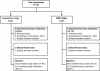
Methods: This 12-month, multicenter, open-label study randomized (1:1) 122 Japanese de-novo RTx patients to either an everolimus regimen (1.5 mg/day starting dose (target trough: 3 to 8 ng/ml) + reduced-dose cyclosporine) or a mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) regimen (2 g/day + standard dose cyclosporine). All patients received basiliximab and corticosteroids. Key endpoints at month 12 were composite efficacy failure (treated biopsy-proven acute rejection, graft loss, death, or loss to follow-up) and renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate; Modification of Diet in Renal Disease-4).
Results: Clear cyclosporine exposure reduction was achieved in the everolimus group throughout the study (52% reduction at month 12). Month 12 efficacy failure rates showed everolimus 1.5 mg to be non-inferior to MMF (11.5% vs. 11.5%). The median estimated glomerular filtration rate at month 12 was 58.00 ml/minute/1.73 m2 in the everolimus group versus 55.25 ml/minute/1.73 m2 in the MMF group (P = 0.063). Overall, the incidence of adverse events was comparable between the groups with some differences in line with the known safety profile of the treatments. The everolimus group had a higher incidence of wound healing events and edema, whereas a higher rate of cytomegalovirus infections was reported in the MMF group.
Conclusions: This study confirmed the efficacy of everolimus 1.5 mg/day (target trough: 3 to 8 ng/ml) in Japanese RTx patients for preventing acute rejection, while allowing for substantial cyclosporine sparing. Renal function and safety findings were comparable with previous reports from other RTx populations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT00658320.
Figures

References
-
- The Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation. Annual progress report from the Japanese renal transplant registry: number of renal transplantations in 2008, part 2. ISYOKU. 2009;44:548.
-
- Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O’Connell PJ, Chapman JR, Allen RD. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity: longitudinal assessment by protocol histology. Transplantation. 2004;78:557. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

