Biological function of Presenilin and its role in AD pathogenesis
- PMID: 23866842
- PMCID: PMC3718700
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-9158-2-15
Biological function of Presenilin and its role in AD pathogenesis
Abstract
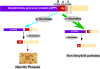
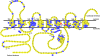
Presenilins (PSs) are the catalytic core of γ-secretase complex. However, the mechanism of FAD-associated PS mutations in AD pathogenesis still remains elusive. Here we review the general biology and mechanism of γ-secretase and focus on the catalytic components - presenilins and their biological functions and contributions to the AD pathogenesis. The functions of presenilins are divided into γ-secretase dependent and γ-secretase independent ones. The γ-secretase dependent functions of presenilins are exemplified by the sequential cleavages in the processing of APP and Notch; the γ-secretase independent functions of presenilins include stabilizing β-catenin in Wnt signaling pathway, regulating calcium homeostasis and their interaction with synaptic transmission.
Figures
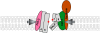

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

