KEAP1-NRF2 complex in ischemia-induced hepatocellular damage of mouse liver transplants
- PMID: 23867319
- PMCID: PMC4524560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.016
KEAP1-NRF2 complex in ischemia-induced hepatocellular damage of mouse liver transplants
Abstract
Background & aims: The Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway regulates host cell defense responses against oxidative stress and maintains the cellular redox balance.
Methods: We investigated the function/molecular mechanisms by which Keap1-Nrf2 complex may influence liver ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) in a mouse model of hepatic cold storage (20h at 4°C) followed by orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT).
Results: The Keap1 hepatocyte-specific knockout (HKO) in the donor liver ameliorated post-transplant IRI, evidenced by improved hepatocellular function and OLT outcomes (Keap1 HKO→Keap1 HKO; 100% survival), as compared with controls (WT→WT; 50% survival; p<0.01). By contrast, donor liver Nrf2 deficiency exacerbated IRI in transplant recipients (Nrf2 KO→Nrf2 KO; 40% survival). Ablation of Keap1 signaling reduced macrophage/neutrophil trafficking, pro-inflammatory cytokine programs, and hepatocellular necrosis/apoptosis, while simultaneously promoting anti-apoptotic functions in OLTs. At the molecular level, Keap1 HKO increased Nrf2 levels, stimulated Akt phosphorylation, and enhanced expression of anti-oxidant Trx1, HIF-1α, and HO-1. Pretreatment of liver donors with PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) disrupted Akt/HIF-1A signaling and recreated hepatocellular damage in otherwise IR-resistant Keap1 HKO transplants. In parallel in vitro studies, hydrogen peroxide-stressed Keap1-deficient hepatocytes were characterized by enhanced expression of Nrf2, Trx1, and Akt phosphorylation, in association with decreased release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in cell culture supernatants.
Conclusions: Keap1-Nrf2 complex prevents oxidative injury in IR-stressed OLTs through Keap1 signaling, which negatively regulates Nrf2 pathway. Activation of Nrf2 induces Trx1 and promotes PI3K/Akt, crucial for HIF-1α activity. HIF-1α-mediated overexpression of HO-1/Cyclin D1 facilitates cytoprotection by limiting hepatic inflammatory responses, and hepatocellular necrosis/apoptosis in a PI3K-dependent manner.
Keywords: ARE; H(2)O(2); HIF-1; HKO; HO-1; HRE; IRI; Keap1; Keap1-Nrf2 redox system; Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LDH; Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury; Liver transplantation; Nrf2; OLT; PI3K; TUNEL; Trx1; anti-oxidant response element; heme-oxygenase-1; hepatocyte knockout; hydrogen peroxide; hypoxia inducible factor-1; hypoxia response element; ischemia/reperfusion injury; lactate dehydrogenase; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; orthotopic liver transplantation; phosphoinositide 3-kinase; sALT; serum alanine aminotransferase; terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labeling; thioredoxin 1.
Copyright © 2013 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
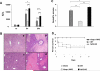
 ) WT WT; (c;
) WT WT; (c;  ) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (d;
) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (d;  ) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. (A) sALT levels. Mean SD; n=4 mice/group. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.0005. (B) Representative OLT histology (H&E; magnification x100); (C) Suzuki's histological grading of IRI (24h). Mean SD; n=4-6 mice/group. *p<0.05, **p<0.001. (D) OLT survival: (■) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO (100%); (◆) WT WT (50%); (▲) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO (40%; p<0.01). N=10 mice/group.
) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. (A) sALT levels. Mean SD; n=4 mice/group. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.0005. (B) Representative OLT histology (H&E; magnification x100); (C) Suzuki's histological grading of IRI (24h). Mean SD; n=4-6 mice/group. *p<0.05, **p<0.001. (D) OLT survival: (■) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO (100%); (◆) WT WT (50%); (▲) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO (40%; p<0.01). N=10 mice/group.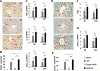
 ) WT WT; (b;
) WT WT; (b;  ) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (c;
) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (c;  ) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. (A/B) Immunohistochemical staining for CD68+ cells. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×400; *p<0.005, **p<0.0001. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted cytokine/chemokine gene expression; Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.005. (D/E) Immunohistochemical staining for LY6G+ cells. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×400; *p<0.001, **p<0.0001. (F) Neutrophil MPO activity (U/gm). Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of CXCL-1. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. (A/B) Immunohistochemical staining for CD68+ cells. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×400; *p<0.005, **p<0.0001. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted cytokine/chemokine gene expression; Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.005. (D/E) Immunohistochemical staining for LY6G+ cells. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×400; *p<0.001, **p<0.0001. (F) Neutrophil MPO activity (U/gm). Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of CXCL-1. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.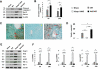
 ) WT WT; (b;
) WT WT; (b;  ) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (c;
) Keap1HKO Keap1HKO; (c;  ) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×200 *p<0.05; **p<0.001. (E) Western analysis of Keap1, Nrf2, Trx1, p-Akt, HIF-1 , and HO-1 in OLTs. β-actin served as an internal control. Representative of three experiments. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of mRNA coding for Trx1, Nqo1 and Gclc. Data were normalized to HPRT gene expression. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
) Nrf2KO Nrf2KO. Representative of 4 mice/group; magnification ×200 *p<0.05; **p<0.001. (E) Western analysis of Keap1, Nrf2, Trx1, p-Akt, HIF-1 , and HO-1 in OLTs. β-actin served as an internal control. Representative of three experiments. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of mRNA coding for Trx1, Nqo1 and Gclc. Data were normalized to HPRT gene expression. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.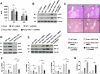
 ) WT+DMSO; (
) WT+DMSO; ( ) WT+ Lly294002; (
) WT+ Lly294002; ( ) Keap1 HKO+DMSO; (
) Keap1 HKO+DMSO; ( ) Keap1 HKO+Ly294002. Mean±SD; n=4 mice/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B) Western analysis of p-Akt and HIF-1 in OLTs. β-actin served as an internal control. Representative of three experiments. (C) Representative H&E staining of OLTs (n=4) at 24h: Panel (a) WT+DMSO; (b) WT+Ly294002; (c) Keap1HKO+DMSO; (d) Keap1HKO+Ly294002 (magnification x100). Keap1-dependent Nrf2 activation promoted Trx1/Akt/HIF-1 signaling in mouse hepatocytes in vitro. (D) Western blot expression of Nrf2, Trx1 and p-Akt in primary H2O2-stressed hepatocyte (WT, Keap1HKO or Nrf2KO) cultures. Representative of three experiments. (E) Primary H2O2-stressed hepatocytes were pretreated with PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) or DMSO; p-Akt/HIF-1 expression was analyzed by Western blots. Representative of three experiments. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of HIF-1 , HO-1, and Cyclin D1 in LY294002/DMSO-pretreated H2O2-stressed hepatocyte cultures. (G) LDH release (U/L) in LY294002/DMSO-treated hepatocytes. (F-G): (□) WT cells; (
) Keap1 HKO+Ly294002. Mean±SD; n=4 mice/group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B) Western analysis of p-Akt and HIF-1 in OLTs. β-actin served as an internal control. Representative of three experiments. (C) Representative H&E staining of OLTs (n=4) at 24h: Panel (a) WT+DMSO; (b) WT+Ly294002; (c) Keap1HKO+DMSO; (d) Keap1HKO+Ly294002 (magnification x100). Keap1-dependent Nrf2 activation promoted Trx1/Akt/HIF-1 signaling in mouse hepatocytes in vitro. (D) Western blot expression of Nrf2, Trx1 and p-Akt in primary H2O2-stressed hepatocyte (WT, Keap1HKO or Nrf2KO) cultures. Representative of three experiments. (E) Primary H2O2-stressed hepatocytes were pretreated with PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) or DMSO; p-Akt/HIF-1 expression was analyzed by Western blots. Representative of three experiments. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR-assisted detection of HIF-1 , HO-1, and Cyclin D1 in LY294002/DMSO-pretreated H2O2-stressed hepatocyte cultures. (G) LDH release (U/L) in LY294002/DMSO-treated hepatocytes. (F-G): (□) WT cells; ( ) WT cells+DMSO; (
) WT cells+DMSO; ( ) WT cells+Ly294002; (
) WT cells+Ly294002; ( ) Keap1 HKO cells; (
) Keap1 HKO cells; ( ) Keap1 HKO cells+DMSO; (
) Keap1 HKO cells+DMSO; ( ) Keap1 HKO cells+Ly294002. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.005, **p<0.0005.
) Keap1 HKO cells+Ly294002. Mean±SD; n=3-4/group; *p<0.005, **p<0.0005.Similar articles
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 regulates toll-like receptor 4 innate responses in mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through Akt-forkhead box protein O1 signaling network.Transplantation. 2014 Oct 15;98(7):721-8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000316. Transplantation. 2014. PMID: 25171655 Free PMC article.
-
ATF3-mediated NRF2/HO-1 signaling regulates TLR4 innate immune responses in mouse liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.Am J Transplant. 2015 Jan;15(1):76-87. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12954. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25359217
-
CD4+ T Cell NRF2 Signaling Improves Liver Transplantation Outcomes by Modulating T Cell Activation and Differentiation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):670-683. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0094. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36070449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Soluble Form of P Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand 1 Requires Signaling by Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 to Protect Liver Transplant Endothelial Cells Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Am J Transplant. 2017 Jun;17(6):1462-1475. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14159. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Am J Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27977895 Free PMC article.
-
Heme Oxygenase-1 in liver transplant ischemia-reperfusion injury: From bench-to-bedside.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Sep;157:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.012. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32084514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Brain Circ. 2016 Apr-Jun;2(2):61-66. doi: 10.4103/2394-8108.186256. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Brain Circ. 2016. PMID: 30276274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PEG35 and Glutathione Improve Mitochondrial Function and Reduce Oxidative Stress in Cold Fatty Liver Graft Preservation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;11(1):158. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010158. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052662 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Fibrosis-From Mechanisms of Injury to Modulation of Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 11;8:814496. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.814496. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35087852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase protects against necroptosis via regulation of Keap1-PGAM5 complex.Int J Cardiol. 2018 May 15;259:153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.01.036. Int J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29579593 Free PMC article.
-
Cold exposure induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in the myocardium by inhibiting the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Feb 15;18(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0748-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29448942 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

