Concurrent TMS to the primary motor cortex augments slow motor learning
- PMID: 23867557
- PMCID: PMC4331120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.024
Concurrent TMS to the primary motor cortex augments slow motor learning
Abstract
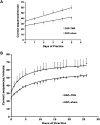
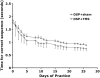
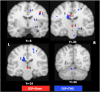
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has shown promise as a treatment tool, with one FDA approved use. While TMS alone is able to up- (or down-) regulate a targeted neural system, we argue that TMS applied as an adjuvant is more effective for repetitive physical, behavioral and cognitive therapies, that is, therapies which are designed to alter the network properties of neural systems through Hebbian learning. We tested this hypothesis in the context of a slow motor learning paradigm. Healthy right-handed individuals were assigned to receive 5 Hz TMS (TMS group) or sham TMS (sham group) to the right primary motor cortex (M1) as they performed daily motor practice of a digit sequence task with their non-dominant hand for 4 weeks. Resting cerebral blood flow (CBF) was measured by H2(15)O PET at baseline and after 4 weeks of practice. Sequence performance was measured daily as the number of correct sequences performed, and modeled using a hyperbolic function. Sequence performance increased significantly at 4 weeks relative to baseline in both groups. The TMS group had a significant additional improvement in performance, specifically, in the rate of skill acquisition. In both groups, an improvement in sequence timing and transfer of skills to non-trained motor domains was also found. Compared to the sham group, the TMS group demonstrated increases in resting CBF specifically in regions known to mediate skill learning namely, the M1, cingulate cortex, putamen, hippocampus, and cerebellum. These results indicate that TMS applied concomitantly augments behavioral effects of motor practice, with corresponding neural plasticity in motor sequence learning network. These findings are the first demonstration of the behavioral and neural enhancing effects of TMS on slow motor practice and have direct application in neurorehabilitation where TMS could be applied in conjunction with physical therapy.
Keywords: Digit sequence practice; Hebbian learning; Hyperbolic function; Motor learning; Motor learning network; Motor system; Primary motor cortex; Skill transfer; TMS.
© 2013.
Figures


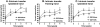
References
-
- Adkins-Muir DL, Jones TA. Cortical electrical stimulation combined with rehabilitative training: enhanced functional recovery and dendritic plasticity following focal cortical ischemia in rats. Neurol. Res. 2003;25(8):780–788. - PubMed
-
- Agostino R, Iezzi E, Dinapoli L, Gilio F, Conte A, Mari F, Berardelli A. Effects of 5 Hz subthreshold magnetic stimulation of primary motor cortex on fast finger movements in normal subjects. Exp. Brain Res. 2007;180(1):105–111. - PubMed
-
- Albouy G, Sterpenich V, Balteau E, Vandewalle G, Desseilles M, ng-Vu T, et al. Both the hippocampus and striatum are involved in consolidation of motor sequence memory. Neuron. 2008;58:261–272. - PubMed
-
- Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;1:1106–1107. - PubMed
-
- Boggio PS, Nunes A, Rigonatti SP, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Fregni F. Repeated sessions of noninvasive brain DC stimulation is associated with motor function improvement in stroke patients. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2007;25(2):123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

