Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system
- PMID: 23868073
- PMCID: PMC6519453
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2013.092
Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system
Abstract
The PANTHER (protein annotation through evolutionary relationship) classification system (http://www.pantherdb.org/) is a comprehensive system that combines gene function, ontology, pathways and statistical analysis tools that enable biologists to analyze large-scale, genome-wide data from sequencing, proteomics or gene expression experiments. The system is built with 82 complete genomes organized into gene families and subfamilies, and their evolutionary relationships are captured in phylogenetic trees, multiple sequence alignments and statistical models (hidden Markov models or HMMs). Genes are classified according to their function in several different ways: families and subfamilies are annotated with ontology terms (Gene Ontology (GO) and PANTHER protein class), and sequences are assigned to PANTHER pathways. The PANTHER website includes a suite of tools that enable users to browse and query gene functions, and to analyze large-scale experimental data with a number of statistical tests. It is widely used by bench scientists, bioinformaticians, computer scientists and systems biologists. In the 2013 release of PANTHER (v.8.0), in addition to an update of the data content, we redesigned the website interface to improve both user experience and the system's analytical capability. This protocol provides a detailed description of how to analyze genome-wide experimental data with the PANTHER classification system.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
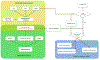

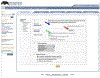

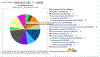


References
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

