Molecular pathways: coexpression of immune checkpoint molecules: signaling pathways and implications for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 23868869
- PMCID: PMC4005613
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1972
Molecular pathways: coexpression of immune checkpoint molecules: signaling pathways and implications for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
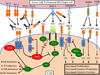
The expression of immune checkpoint molecules on T cells represents an important mechanism that the immune system uses to regulate responses to self-proteins. Checkpoint molecules include cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4, programmed death-1, lymphocyte activation gene-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin protein-3, and several others. Previous studies have identified individual roles for each of these molecules, but more recent data show that coexpression of checkpoint molecules occurs frequently on cancer-specific T cells as well as on pathogen-specific T cells in chronic infections. As the signaling pathways associated with each checkpoint molecule have not been fully elucidated, blocking multiple checkpoints with specific monoclonal antibodies results in improved outcomes in several chronic viral infections as well as in a wide array of preclinical models of cancer. Recent clinical data suggest similar effects in patients with metastatic melanoma. These findings support the concept that individual immune checkpoint molecules may function through nonoverlapping molecular mechanisms. Here, we review current data regarding immune checkpoint molecule signaling and coexpression, both in cancer and infectious disease, as well as the results of preclinical and clinical manipulations of checkpoint proteins.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Relevant Conflicts of Interest:
CJN – none. CGD has served as a paid consultant to Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), CoStim Inc, and Pfizer. CGD has also received sponsored research funding from BMS. These relationships are managed through the Johns Hopkins Conflict of Interest Committee.
Figures
References
-
- Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R, Freeman GJ. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

