Prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among individuals with CKD
- PMID: 23868902
- PMCID: PMC3805064
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00550113
Prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among individuals with CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: Apparent treatment-resistant hypertension is defined as systolic/diastolic BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg with concurrent use of three or more antihypertensive medication classes or use of four or more antihypertensive medication classes regardless of BP level.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: The prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke study participants treated for hypertension (n=10,700) was determined by level of estimated GFR and albumin-to-creatinine ratio, and correlates of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among those participants with CKD were evaluated. CKD was defined as an albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥ 30 mg/g or estimated GFR<60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2).
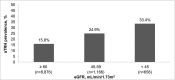
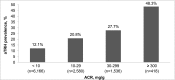
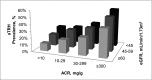
Results: The prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension was 15.8%, 24.9%, and 33.4% for those participants with estimated GFR ≥ 60, 45-59, and <45 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), respectively, and 12.1%, 20.8%, 27.7%, and 48.3% for albumin-to-creatinine ratio<10, 10-29, 30-299, and ≥ 300 mg/g, respectively. The multivariable-adjusted prevalence ratios (95% confidence intervals) for apparent treatment-resistant hypertension were 1.25 (1.11 to 1.41) and 1.20 (1.04 to 1.37) for estimated GFR levels of 45-59 and <45 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), respectively, versus ≥ 60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) and 1.54 (1.39 to 1.71), 1.76 (1.57 to 1.97), and 2.44 (2.12 to 2.81) for albumin-to-creatinine ratio levels of 10-29, 30-299, and ≥ 300 mg/g, respectively, versus albumin-to-creatinine ratio<10 mg/g. After multivariable adjustment, men, black race, larger waist circumference, diabetes, history of myocardial infarction or stroke, statin use, and lower estimated GFR and higher albumin-to-creatinine ratio levels were associated with apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among individuals with CKD.
Conclusions: This study highlights the high prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among individuals with CKD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes and CKD in the United States Population, 2009-2014.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Dec 7;12(12):1984-1990. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03700417. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 29054846 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic kidney disease and incident apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among blacks: Data from the Jackson Heart Study.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2017 Nov;19(11):1117-1124. doi: 10.1111/jch.13065. Epub 2017 Sep 17. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2017. PMID: 28921875 Free PMC article.
-
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Phenotypes in Adults Taking Antihypertensive Medication with and without CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Apr 7;15(4):501-510. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08840719. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32217635 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Function Decline and Apparent Treatment-Resistant Hypertension in the Elderly.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 25;11(1):e0146056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146056. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26807712 Free PMC article.
-
Incident ESRD and treatment-resistant hypertension: the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke (REGARDS) study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 May;63(5):781-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.11.016. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24388119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aldosterone-targeted therapies: early implementation in resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease.Eur Heart J. 2025 Jul 14;46(27):2618-2642. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf225. Eur Heart J. 2025. PMID: 40214750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apparent Treatment-Resistant Hypertension in the First Year Associated With Cardiovascular Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients.Am J Hypertens. 2024 Jun 14;37(7):514-522. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpae010. Am J Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38252960 Free PMC article.
-
New Molecules for Treating Resistant Hypertension: a Clinical Perspective.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019 Sep 10;21(10):80. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0978-z. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019. PMID: 31506798 Review.
-
Preferred Fourth-Line Pharmacotherapy for Resistant Hypertension: Are We There Yet?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Apr;19(4):30. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0728-z. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28349377 Review.
-
Psychosocial correlates of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension in the Jackson Heart Study.J Hum Hypertens. 2017 Jul;31(7):486. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2017.19. J Hum Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28588315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parikh NI, Hwang SJ, Larson MG, Meigs JB, Levy D, Fox CS: Cardiovascular disease risk factors in chronic kidney disease: Overall burden and rates of treatment and control. Arch Intern Med 166: 1884–1891, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Wei GL, McQuillan G, Brancati FL, Levey AS, Jones C, Klag MJ: Prevalence of high blood pressure and elevated serum creatinine level in the United States: Findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988–1994). Arch Intern Med 161: 1207–1216, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Muntner P, Anderson A, Charleston J, Chen Z, Ford V, Makos G, O'Connor A, Perumal K, Rahman M, Steigerwalt S, Teal V, Townsend R, Weir M, Wright JT, Jr, Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Investigators : Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in adults with CKD: Results from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. Am J Kidney Dis 55: 441–451, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM: Resistant hypertension: Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension 51: 1403–1419, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

