An inducible transgenic mouse model for immune mediated hepatitis showing clearance of antigen expressing hepatocytes by CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 23869228
- PMCID: PMC3711822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068720
An inducible transgenic mouse model for immune mediated hepatitis showing clearance of antigen expressing hepatocytes by CD8+ T cells
Abstract
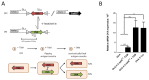
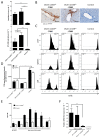
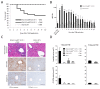
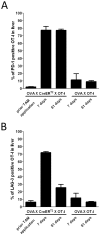
The liver has the ability to prime immune responses against neo antigens provided upon infections. However, T cell immunity in liver is uniquely modulated by the complex tolerogenic property of this organ that has to also cope with foreign agents such as endotoxins or food antigens. In this respect, the nature of intrahepatic T cell responses remains to be fully characterized. To gain deeper insight into the mechanisms that regulate the CD8+ T cell responses in the liver, we established a novel OVA_X_CreER(T2) mouse model. Upon tamoxifen administration OVA antigen expression is observed in a fraction of hepatocytes, resulting in a mosaic expression pattern. To elucidate the cross-talk of CD8+ T cells with antigen-expressing hepatocytes, we adoptively transferred K(b)/OVA257-264-specific OT-I T cells to OVA_X_CreER(T2) mice or generated triple transgenic OVA_X CreER(T2)_X_OT-I mice. OT-I T cells become activated in OVA_X_CreER(T2) mice and induce an acute and transient hepatitis accompanied by liver damage. In OVA_X_CreER(T2)_X_OT-I mice, OVA induction triggers an OT-I T cell mediated, fulminant hepatitis resulting in 50% mortality. Surviving mice manifest a long lasting hepatitis, and recover after 9 weeks. In these experimental settings, recovery from hepatitis correlates with a complete loss of OVA expression indicating efficient clearance of the antigen-expressing hepatocytes. Moreover, a relapse of hepatitis can be induced upon re-induction of cured OVA_X_CreER(T2)_X_OT-I mice indicating absence of tolerogenic mechanisms. This pathogen-free, conditional mouse model has the advantage of tamoxifen inducible tissue specific antigen expression that reflects the heterogeneity of viral antigen expression and enables the study of intrahepatic immune responses to both de novo and persistent antigen. It allows following the course of intrahepatic immune responses: initiation, the acute phase and antigen clearance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Crispe IN (2003) Hepatic T cells and liver tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 3: 51-62. doi:10.1038/nri981. PubMed: 12511875. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thomson AW, Knolle PA (2010) Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat Rev Immunol 10: 753-766. doi:10.1038/nri2858. PubMed: 20972472. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rehermann B, Nascimbeni M (2005) Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 215-229. doi:10.1038/nri1573. PubMed: 15738952. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

