Sulfur amino acids regulate translational capacity and metabolic homeostasis through modulation of tRNA thiolation
- PMID: 23870129
- PMCID: PMC3757545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.043
Sulfur amino acids regulate translational capacity and metabolic homeostasis through modulation of tRNA thiolation
Abstract
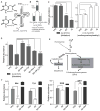
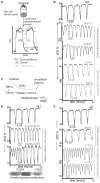
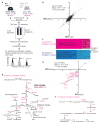
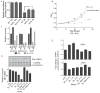
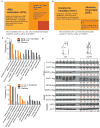
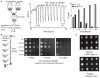
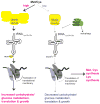
Protein translation is an energetically demanding process that must be regulated in response to changes in nutrient availability. Herein, we report that intracellular methionine and cysteine availability directly controls the thiolation status of wobble-uridine (U34) nucleotides present on lysine, glutamine, or glutamate tRNAs to regulate cellular translational capacity and metabolic homeostasis. tRNA thiolation is important for growth under nutritionally challenging environments and required for efficient translation of genes enriched in lysine, glutamine, and glutamate codons, which are enriched in proteins important for translation and growth-specific processes. tRNA thiolation is downregulated during sulfur starvation in order to decrease sulfur consumption and growth, and its absence leads to a compensatory increase in enzymes involved in methionine, cysteine, and lysine biosynthesis. Thus, tRNA thiolation enables cells to modulate translational capacity according to the availability of sulfur amino acids, establishing a functional significance for this conserved tRNA nucleotide modification in cell growth control.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
tRNA wobble-uridine modifications as amino acid sensors and regulators of cellular metabolic state.Curr Genet. 2020 Jun;66(3):475-480. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01045-y. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 31758251 Review.
-
tRNA thiolation links translation to stress responses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Jan 15;26(2):270-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-06-1145. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25392298 Free PMC article.
-
Cbr1 is a Dph3 reductase required for the tRNA wobble uridine modification.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Dec;12(12):995-997. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2190. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27694803 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-related modifier Urm1 acts as a sulphur carrier in thiolation of eukaryotic transfer RNA.Nature. 2009 Mar 12;458(7235):228-32. doi: 10.1038/nature07643. Epub 2009 Jan 14. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19145231
-
Sulfur Modifications of the Wobble U34 in tRNAs and their Intracellular Localization in Eukaryotic Cells.Biomolecules. 2017 Feb 18;7(1):17. doi: 10.3390/biom7010017. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28218716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methionine metabolism in health and cancer: a nexus of diet and precision medicine.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Nov;19(11):625-637. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0187-8. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31515518 Review.
-
Genome recoding by tRNA modifications.Open Biol. 2016 Dec;6(12):160287. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160287. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27974624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methionine restriction constrains lipoylation and activates mitochondria for nitrogenic synthesis of amino acids.Nat Commun. 2023 May 2;14(1):2504. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38289-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37130856 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Function and Metabolomics Study in Mice after Dietary Supplementation with Methionine.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 20;2020:9494528. doi: 10.1155/2020/9494528. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33145362 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur sequestration promotes multicellularity during nutrient limitation.Nature. 2021 Mar;591(7850):471-476. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03270-3. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33627869 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

