Genome-wide generation and systematic phenotyping of knockout mice reveals new roles for many genes
- PMID: 23870131
- PMCID: PMC3717207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.022
Genome-wide generation and systematic phenotyping of knockout mice reveals new roles for many genes
Abstract
Mutations in whole organisms are powerful ways of interrogating gene function in a realistic context. We describe a program, the Sanger Institute Mouse Genetics Project, that provides a step toward the aim of knocking out all genes and screening each line for a broad range of traits. We found that hitherto unpublished genes were as likely to reveal phenotypes as known genes, suggesting that novel genes represent a rich resource for investigating the molecular basis of disease. We found many unexpected phenotypes detected only because we screened for them, emphasizing the value of screening all mutants for a wide range of traits. Haploinsufficiency and pleiotropy were both surprisingly common. Forty-two percent of genes were essential for viability, and these were less likely to have a paralog and more likely to contribute to a protein complex than other genes. Phenotypic data and more than 900 mutants are openly available for further analysis. PAPERCLIP:
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

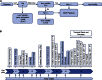
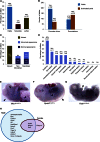
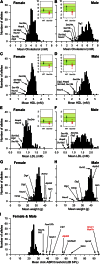
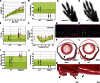

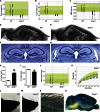
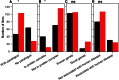

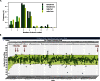
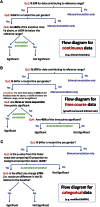
References
-
- Abou Jamra R., Philippe O., Raas-Rothschild A., Eck S.H., Graf E., Buchert R., Borck G., Ekici A., Brockschmidt F.F., Nöthen M.M. Adaptor protein complex 4 deficiency causes severe autosomal-recessive intellectual disability, progressive spastic paraplegia, shy character, and short stature. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;88:788–795. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayadi A., Birling M.C., Bottomley J., Bussell J., Fuchs H., Fray M., Gailus-Durner V., Greenaway S., Houghton R., Karp N. Mouse large-scale phenotyping initiatives: overview of the European Mouse Disease Clinic (EUMODIC) and of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Mouse Genetics Project. Mamm. Genome. 2012;23:600–610. - PMC - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Erdfelder E., Faul F., Buchner A. GPOWER: a general power analysis program. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1996;28:1–11.
-
- Käll L., Krogh A., Sonnhammer E.L. A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;338:1027–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EY018213/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- G0300212/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K08 EY020530/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- RG45277 PCAG/116/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 5K08EY020530-02/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 12401/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- EY08213/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137918/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 13031/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 096540/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 100669/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

