Genome-wide linkage analysis of carotid artery lumen diameter: the strong heart family study
- PMID: 23871337
- PMCID: PMC4028022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.06.048
Genome-wide linkage analysis of carotid artery lumen diameter: the strong heart family study
Abstract
Background: A significant proportion of the variability in carotid artery lumen diameter is attributable to genetic factors.
Methods: Carotid ultrasonography and genotyping were performed in the 3300 American Indian participants in the Strong Heart Family Study (SHFS) to identify chromosomal regions harboring novel genes associated with inter-individual variation in carotid artery lumen diameter. Genome-wide linkage analysis was conducted using standard variance component linkage methods, implemented in SOLAR, based on multipoint identity-by-descent matrices.
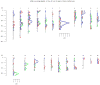
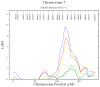
Results: Genome-wide linkage analysis revealed a significant evidence for linkage for a locus for left carotid artery diastolic and systolic lumen diameters in Arizona SHFS participants on chromosome 7 at 120 cM (lod = 4.85 and 3.77, respectively, after sex and age adjustment, and lod = 3.12 and 2.72, respectively, after adjustment for sex, age, height, weight, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and current smoking). Other regions with suggestive evidence of linkage for left carotid artery diastolic and systolic lumen diameter were found on chromosome 12 at 153 cM (lod = 2.20 and 2.60, respectively, after sex and age adjustment, and lod = 2.44 and 2.16, respectively, after full covariate adjustment) in Oklahoma SHFS participants; suggestive linkage for right carotid artery diastolic and systolic lumen diameter was found on chromosome 9 at 154 cM (lod = 2.72 and 3.19, respectively after sex and age adjustment, and lod = 2.36 and 2.21, respectively, after full covariate adjustment) in Oklahoma SHFS participants.
Conclusion: We found significant evidence for loci influencing carotid artery lumen diameter on chromosome 7q and suggestive linkage on chromosomes 12q and 9q.
Keywords: Carotid artery; Genetics; Linkage analysis; Ultrasonography; Variance components.
© 2013. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes-specific genetic effects on obesity traits in American Indian populations: the Strong Heart Family Study.BMC Med Genet. 2008 Oct 14;9:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-9-90. BMC Med Genet. 2008. PMID: 18854016 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage analysis of albuminuria.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Jul;20(7):1597-606. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008080895. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19369405 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage study of fibrinogen levels: the Strong Heart Family Study.BMC Med Genet. 2008 Aug 12;9:77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-9-77. BMC Med Genet. 2008. PMID: 18700015 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic influence on variation in serum uric acid in American Indians: the strong heart family study.Hum Genet. 2009 Nov;126(5):667-76. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0716-8. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19590895 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art review on automated lumen and adventitial border delineation and its measurements in carotid ultrasound.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Sep;163:155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.05.015. Epub 2018 May 11. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30119850 Review.
Cited by
-
PRIMUS: rapid reconstruction of pedigrees from genome-wide estimates of identity by descent.Am J Hum Genet. 2014 Nov 6;95(5):553-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 25439724 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics approaches for revealing the complexity of cardiovascular disease.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab061. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab061. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33725119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Greater Height Is Associated with a Larger Carotid Lumen Diameter.Medicines (Basel). 2019 May 14;6(2):57. doi: 10.3390/medicines6020057. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31091706 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between sirtuin and mitochondrial uncoupling protein genes and carotid artery stiffness.Transl Res. 2015 Feb;165(2):358-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25258298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diabetes and Associated Cardiovascular Complications in American Indians/Alaskan Natives: A Review of Risks and Prevention Strategies.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Sep 13;2018:2742565. doi: 10.1155/2018/2742565. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30302343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roman MJ, Saba PS, Pini R, et al. Parallel cardiac and vascular adaptation in hypertension. Circulation. 1992;86:1909–1918. - PubMed
-
- Salonen JT, Salonen R. Ultrasonographically assessed carotid morphology and risk of coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1991;11:1245–1249. - PubMed
-
- Belcaro G, Nicolaides AN, Laurora G, Cesarone MR, De Sanctis M, Incandela L, Barsotti A. Ultrasound morphology classification of the arterial wall and cardiovascular events in a 6-year follow-up study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996;16:851–856. - PubMed
-
- Greenland P, Abrams J, Aurigemma GP, et al. Prevention Conference V: beyond secondary prevention: identifying the high-risk patient for primary prevention noninvasive tests of atherosclerotic burden. Circulation. 2002;101:e16–e22. - PubMed
-
- Johnsen SH, Joakimsen O, Singh K, Stensland E, Forsdahl SH, Jacobsen BK. Relation of common carotid artery lumen diameter to general arterial dilating diathesis and abdominal aortic aneurysms: The Tromsø Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;169:330–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HL65521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL041642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000047/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL41654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109319/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL41642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL065520/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL41652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL041654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL041652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M10RR0047-34/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL65520/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL065521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

