MicroRNA modulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in cardiometabolic diseases
- PMID: 23871755
- PMCID: PMC4145589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.014
MicroRNA modulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in cardiometabolic diseases
Abstract
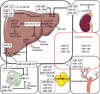
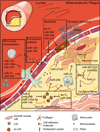
The regulation of the metabolism of cholesterol has been one of the most studied biological processes since its first isolation from gallstones in 1784. High levels of plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and reduced levels of plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol are widely recognized as major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. An imbalance in the production of reactive oxygen species can oxidize LDL particles, increasing the levels of the highly proatherogenic oxidized LDL. Furthermore, under pathological scenarios, numerous molecules can function as pro-oxidants, such as iron or (high levels of) glucose. In addition to the classical mechanisms regulating lipid homeostasis, recent studies have demonstrated the important role of microRNAs (miRNAs) as regulators of lipoprotein metabolism, oxidative derivatives of lipoprotein, and redox balance. Here, we summarize recent findings in the field, highlighting the contributions of some miRNAs to lipid- and oxidative-associated pathologies. We also discuss how therapeutic intervention of miRNAs may be a promising strategy to decrease LDL, increase HDL, and ameliorate lipid- and oxidative-related disorders, including atherosclerosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Free radicals; Lipid metabolism; MiRNAs.
© 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNAs in lipoprotein metabolism and cardiometabolic disorders.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Mar;246:352-60. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.01.025. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 26828754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis: the role of microRNAs in arterial remodeling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;64:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23797034 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar 22;13(4):239-50. doi: 10.1038/nrm3313. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22436747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and lipid metabolism.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2017 Jun;28(3):273-280. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000420. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2017. PMID: 28333713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Human Cytoglobin Prevents Atherosclerosis by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Mar;23(2):162-173. doi: 10.1177/1074248417724870. Epub 2017 Sep 27. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 28954528
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Profile of HCV Spontaneous Clarified Individuals, Denotes Previous HCV Infection.J Clin Med. 2019 Jun 14;8(6):849. doi: 10.3390/jcm8060849. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31207946 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder and Immune Response.J Immunol Res. 2018 Feb 1;2018:2835761. doi: 10.1155/2018/2835761. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29484304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid metabolism, apoptosis and cancer therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 2;16(1):924-49. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010924. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25561239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of oxidative stress status by lipoprotein apheresis in Chinese patients with familial hypercholesterolemia.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 May;34(5):e23161. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23161. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31859412 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical Detection of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy with MicroRNAs: Challenges and Perspectives.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:6143129. doi: 10.1155/2016/6143129. Epub 2015 Dec 6. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 26770988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

