Evolution of cytochrome bc complexes: from membrane-anchored dehydrogenases of ancient bacteria to triggers of apoptosis in vertebrates
- PMID: 23871937
- PMCID: PMC3839093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.07.006
Evolution of cytochrome bc complexes: from membrane-anchored dehydrogenases of ancient bacteria to triggers of apoptosis in vertebrates
Abstract
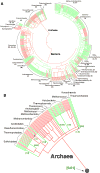
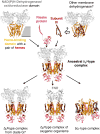
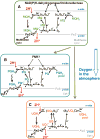
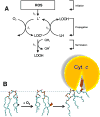
This review traces the evolution of the cytochrome bc complexes from their early spread among prokaryotic lineages and up to the mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex (complex III) and its role in apoptosis. The results of phylogenomic analysis suggest that the bacterial cytochrome b6f-type complexes with short cytochromes b were the ancient form that preceded in evolution the cytochrome bc1-type complexes with long cytochromes b. The common ancestor of the b6f-type and the bc1-type complexes probably resembled the b6f-type complexes found in Heliobacteriaceae and in some Planctomycetes. Lateral transfers of cytochrome bc operons could account for the several instances of acquisition of different types of bacterial cytochrome bc complexes by archaea. The gradual oxygenation of the atmosphere could be the key evolutionary factor that has driven further divergence and spread of the cytochrome bc complexes. On the one hand, oxygen could be used as a very efficient terminal electron acceptor. On the other hand, auto-oxidation of the components of the bc complex results in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which necessitated diverse adaptations of the b6f-type and bc1-type complexes, as well as other, functionally coupled proteins. A detailed scenario of the gradual involvement of the cardiolipin-containing mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex into the intrinsic apoptotic pathway is proposed, where the functioning of the complex as an apoptotic trigger is viewed as a way to accelerate the elimination of the cells with irreparably damaged, ROS-producing mitochondria. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Respiratory complex III and related bc complexes.
Keywords: Bioenergetics, molecular evolution, ubiquinol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase; cardiolipin, cell death, photosynthesis, apoptosome; cytochrome c; plastoquinone; ubiquinone.
© 2013.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial complex III and related bc-complexes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1257. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.08.002. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24053945 No abstract available.
-
Activated Q-cycle as a common mechanism for cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome b6f complexes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1797(12):1858-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.07.008. Epub 2010 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20650262 Review.
-
Structural analysis of cytochrome bc1 complexes: implications to the mechanism of function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1278-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23201476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmembrane signaling and assembly of the cytochrome b6f-lipidic charge transfer complex.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1295-308. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23507619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and use of photoactive ruthenium complexes to study electron transfer within cytochrome bc1 and from cytochrome bc1 to cytochrome c.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1309-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22985600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalytic Reactions and Energy Conservation in the Cytochrome bc1 and b6f Complexes of Energy-Transducing Membranes.Chem Rev. 2021 Feb 24;121(4):2020-2108. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00712. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33464892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative proteomic analysis reveals alterations in development and photosynthesis-related proteins in diploid and triploid rice.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Sep 13;16(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0891-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27619227 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Fluorescent Mitochondria-Targeted Probe MitoCLox Reports Lipid Peroxidation in Response to Oxidative Stress In Vivo.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Feb 10;2020:3631272. doi: 10.1155/2020/3631272. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32104531 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Antioxidants on Cardiolipin Oxidation in Liposomes: Why Mitochondrial Cardiolipin Serves as an Apoptotic Signal?Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8679469. doi: 10.1155/2016/8679469. Epub 2016 May 26. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27313834 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of evolutionarily conserved but functionally uncharacterized membrane proteins in archaea: Prediction of novel components of secretion, membrane remodeling and glycosylation systems.Biochimie. 2015 Nov;118:302-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25583072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry EA, Guergova-Kuras M, Huang LS, Crofts AR. Structure and function of cytochrome bc complexes. Ann Rev Biochem. 2000;69:1005–1075. - PubMed
-
- Al-Attar S, de Vries S. Energy transduction by respiratory metallo-enzymes: From molecular mechanism to cell physiology. Coord Chem Rev. 2012;257:64–80.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

