Increased carbonylation of the lipid phosphatase PTEN contributes to Akt2 activation in a murine model of early alcohol-induced steatosis
- PMID: 23872024
- PMCID: PMC3859727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.011
Increased carbonylation of the lipid phosphatase PTEN contributes to Akt2 activation in a murine model of early alcohol-induced steatosis
Abstract
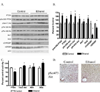
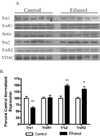
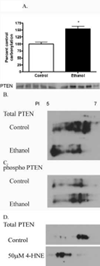
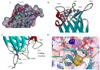
The production of reactive aldehydes such as 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) is a key event in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease (ALD), which ranges from simple steatosis to fibrosis. The lipid phosphatase PTEN plays a central role in the regulation of lipid metabolism in the liver. In this study, the effects of chronic ethanol feeding and carbonylation on the PTEN signaling pathway were examined in a 9-week mouse feeding model for ALD. Chronic ethanol consumption resulted in altered redox homeostasis as evidenced by decreased GSH, decreased Trx1, and increased GST activity. Both PTEN expression and PTEN phosphorylation were significantly increased in the livers of ethanol-fed mice. Carbonylation of PTEN increased significantly in the ethanol-fed mice compared to pair-fed control animals, corresponding to decreased PTEN 3-phosphatase activity. Concomitantly, increased expression of Akt2 along with increased Akt phosphorylation at residues Thr(308), Thr(450), and Ser(473) was observed resulting in increased Akt2 activity in the ethanol-fed animals. Akt2 activation corresponded to a decrease in cytosolic SREBP and ChREBP. Subsequent LC/MS/MS analysis of 4-HNE-modified recombinant human PTEN identified Michael addition adducts of 4-HNE on Cys(71), Cys(136), Lys(147), Lys(223), Cys(250), Lys(254), Lys(313), Lys(327), and Lys(344). Computational-based molecular modeling analysis of 4-HNE adducted to Cys(71) near the active site and Lys(327) in the C2 domain of PTEN suggested inhibition of enzyme catalysis via either stearic hindrance of the active-site pocket or prevention of C2 domain-dependent PTEN function. We hypothesize that 4-HNE-mediated PTEN inhibition contributes to the observed activation of Akt2, suggesting a possible novel mechanism of lipid accumulation in response to increased reactive aldehyde production during chronic ethanol administration in mice.
Keywords: 4-HNE; 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; ALD; ALT; Alcoholic liver disease; ChREBP; Free radicals; Lipid peroxidation; NASH; PI3K; PTEN; PTP; PtdIns(3,4,5)P(3); SREBP; Steatosis; Trx; TrxR; alanine aminotransferase; alcoholic liver disease; carbohydrate response element-binding protein; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; protein tyrosine phosphatase; sterol-response element-binding protein; thioredoxin; thioredoxin reductase.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Seki S, Kitada T, Yamada T, Sakaguchi H, Nakatani K, Wakasa K. In situ detection of lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2002;37:56–62. - PubMed
-
- Seki S, Kitada T, Sakaguchi H. Clinicopathological significance of oxidative cellular damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. Hepatol Res. 2005;33:132–134. - PubMed
-
- Li CJ, Nanji AA, Siakotos AN, Lin RC. Acetaldehyde-modified and 4- hydroxynonenal-modified proteins in the livers of rats with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1997;26:650–657. - PubMed
-
- Hartley DP, Petersen DR. Co-metabolism of ethanol, ethanol-derived acetaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal in isolated rat hepatocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997;21:298–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

