The carbohydrate metabolism signature of lactococcus lactis strain A12 reveals its sourdough ecosystem origin
- PMID: 23872564
- PMCID: PMC3811347
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01560-13
The carbohydrate metabolism signature of lactococcus lactis strain A12 reveals its sourdough ecosystem origin
Abstract
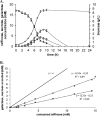
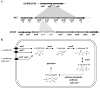
Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain A12 was isolated from sourdough. Combined genomic, transcriptomic, and phenotypic analyses were performed to understand its survival capacity in the complex sourdough ecosystem and its role in the microbial community. The genome sequence comparison of strain A12 with strain IL1403 (a derivative of an industrial dairy strain) revealed 78 strain-specific regions representing 23% of the total genome size. Most of the strain-specific genes were involved in carbohydrate metabolism and are potentially required for its persistence in sourdough. Phenotype microarray, growth tests, and analysis of glycoside hydrolase content showed that strain A12 fermented plant-derived carbohydrates, such as arabinose and α-galactosides. Strain A12 exhibited specific growth rates on raffinose that were as high as they were on glucose and was able to release sucrose and galactose outside the cell, providing soluble carbohydrates for sourdough microflora. Transcriptomic analysis identified genes specifically induced during growth on raffinose and arabinose and reveals an alternative pathway for raffinose assimilation to that used by other lactococci.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In situ activity of a bacteriocin-producing Lactococcus lactis strain. Influence on the interactions between lactic acid bacteria during sourdough fermentation.J Appl Microbiol. 2005;99(3):670-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02647.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16108809
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis A12, a Strain Isolated from Wheat Sourdough.Genome Announc. 2016 Sep 15;4(5):e00692-16. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00692-16. Genome Announc. 2016. PMID: 27634985 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular description and industrial potential of Tn6098 conjugative transfer conferring alpha-galactoside metabolism in Lactococcus lactis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jan;77(2):555-63. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02283-10. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21115709 Free PMC article.
-
Anaerobic sugar catabolism in Lactococcus lactis: genetic regulation and enzyme control over pathway flux.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Oct;60(1-2):24-32. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1065-x. Epub 2002 Sep 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12382039 Review.
-
Physical and genetic maps of the chromosome of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain IL1403 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris strain MG1363.Dev Biol Stand. 1995;85:597-603. Dev Biol Stand. 1995. PMID: 8586238 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Chufa Drink: Potential in Developing a New Plant-Based Fermented Dessert.Foods. 2021 Dec 5;10(12):3010. doi: 10.3390/foods10123010. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34945561 Free PMC article.
-
Lactococcus lactis, a bacterium with probiotic functions and pathogenicity.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 30;39(12):325. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03771-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37776350 Review.
-
Application of antifungal lactobacilli in combination with coatings based on apple processing by-products as a bio-preservative in wheat bread production.J Food Sci Technol. 2019 Jun;56(6):2989-3000. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03775-w. Epub 2019 May 4. J Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31205354 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition Mechanism of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the Growth and Biogenic Amine Production in Morganella morganii.Foods. 2023 Sep 29;12(19):3625. doi: 10.3390/foods12193625. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37835277 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of a Transcriptional Repressor by an Insertion Sequence Element Integration Leads to Activation of a Novel Silent Cellobiose Transporter in Lactococcus lactis MG1363.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Nov 16;83(23):e01279-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01279-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28970222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teuber M, Geis A. 2006. The genus Lactococcus, p 205–228 In Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E. (ed), The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, NY
-
- Gutiérrez-Méndez N, Rodríguez-Figueroa JC, González-Córdova AF, Nevárez-Moorillón GV, Rivera-Chavira B, Vallejo-Cordoba B. 2010. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Lactococcus lactis strains isolated from different ecosystems. Can. J. Microbiol. 56:432–439 - PubMed
-
- Nomura M, Kobayashi M, Narita T, Kimoto-Nira H, Okamoto T. 2006. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Lactococcus lactis from milk and plants. J. Appl. Microbiol. 101:396–405 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

