Independent specialization of the human and mouse X chromosomes for the male germ line
- PMID: 23872635
- PMCID: PMC3758364
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2705
Independent specialization of the human and mouse X chromosomes for the male germ line
Abstract
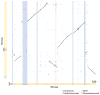
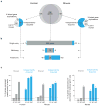
We compared the human and mouse X chromosomes to systematically test Ohno's law, which states that the gene content of X chromosomes is conserved across placental mammals. First, we improved the accuracy of the human X-chromosome reference sequence through single-haplotype sequencing of ampliconic regions. The new sequence closed gaps in the reference sequence, corrected previously misassembled regions and identified new palindromic amplicons. Our subsequent analysis led us to conclude that the evolution of human and mouse X chromosomes was bimodal. In accord with Ohno's law, 94-95% of X-linked single-copy genes are shared by humans and mice; most are expressed in both sexes. Notably, most X-ampliconic genes are exceptions to Ohno's law: only 31% of human and 22% of mouse X-ampliconic genes had orthologs in the other species. X-ampliconic genes are expressed predominantly in testicular germ cells, and many were independently acquired since divergence from the common ancestor of humans and mice, specializing portions of their X chromosomes for sperm production.
Figures

References
-
- Ohno S. Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes. Springer; Berlin: 1967.
-
- Kuroiwa A, et al. Conservation of the rat X chromosome gene order in rodent species. Chromosome Res. 2001;9:61–7. - PubMed
-
- Delgado CL, Waters PD, Gilbert C, Robinson TJ, Graves JA. Physical mapping of the elephant X chromosome: conservation of gene order over 105 million years. Chromosome Res. 2009;17:917–26. - PubMed
-
- Prakash B, Kuosku V, Olsaker I, Gustavsson I, Chowdhary BP. Comparative FISH mapping of bovine cosmids to reindeer chromosomes demonstrates conservation of the X-chromosome. Chromosome Res. 1996;4:214–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

