Estimating Human Cases of Avian Influenza A(H7N9) from Poultry Exposure
- PMID: 23873126
- PMCID: PMC3712490
- DOI: 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.264e737b489bef383fbcbaba60daf928
Estimating Human Cases of Avian Influenza A(H7N9) from Poultry Exposure
Abstract
In March 2013 an outbreak of avian influenza A(H7N9) was first recognized in China. To date there have been 130 cases in human, 47% of which are in men over the age of 55.The influenza strain is a novel subtype not seen before in humans; little is known about zoonotic transmission of the virus, but it is hypothesized that contact with poultry in live bird markets may be a source of exposure. The purpose of this study is to estimate the transmissibility of the virus from poultry to humans by estimating the amount of time shoppers, farmers, and live bird market retailers spend exposed to poultry each day. Results suggest that increased risk among older men is not due to greater exposure time at live bird markets.
Figures
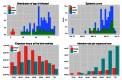
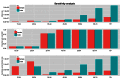
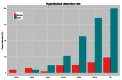
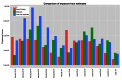
References
-
- Arima Y, Zu R, Murkjekar M, Vong S, Shimada T, et al. Human infections with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus in China preliminary assessments of the age and sex distribution. Western Pacific Surveillance and Response Journal, 2013, 4(2). 10.5365/wpsar.2013.4.2.00510.5365/wpsar.2013.4.2.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emergence of Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus Causing Severe Human Illness — China, February–April 2013. (2013, May 1). Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved May 7, 2013 from http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm62e0501a1.htm - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frequently Asked Questions on human infection caused by the avian influenza A(H7N9) virus. (2013, April 30). World Health Organization. Retrieved May 7, 2013 from Frequently Asked Questions on human infection caused by the avian influenza A(H7N9) virus
-
- Kageyama T, Fujisaki S, Takashita E, Xu H, Yamada S, Uchida Y, Neumann G, Saito T, Kawaoka Y, Tashiro M. (2013, April 11). Genetic analysis of novel avian A(H7N9) influenza viruses isolated from patients in China, February to April 2013. Euro Surveillance. Retrieved April 22, 2013, from http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20453 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frequently Asked Questions on human infection caused by the avian influenza A(H7N9) virus. (2013, April 30). World Health Organization. Retrieved May 7, 2013 from Frequently Asked Questions on human infection caused by the avian influenza A(H7N9) virus
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

