Surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis: open versus minimally invasive surgery
- PMID: 23873608
- PMCID: PMC3773131
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-3171-8
Surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis: open versus minimally invasive surgery
Figures
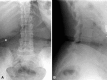

References
-
- Kornblum M, Fischgrund JS. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine (Phila, PA 1976). 2004;29:726–734. - PubMed
-
- Lawton CD, Smith ZA, Barnawi A, Fessler RG. The surgical technique of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Sci. 2011;55:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Lucio JC, Vanconia RB, DeLuzio KJ, Lehmen JA, Rodgers JA, Rodgers W. Economics of less invasive spinal surgery: an analysis of hospital cost differences between open and minimally invasive instrumented spinal fusion procedures during the perioperative period. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2012;5–65–74. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

