Staphylococcus aureus Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 Can Use Depsi-Lipid II Derived from Vancomycin-Resistant Strains for Cell Wall Synthesis
- PMID: 23873669
- PMCID: PMC4235313
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201301074
Staphylococcus aureus Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 Can Use Depsi-Lipid II Derived from Vancomycin-Resistant Strains for Cell Wall Synthesis
Abstract
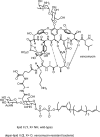
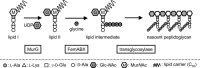
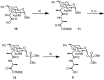
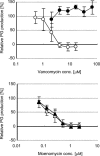
Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) (VRSA) uses depsipeptide-containing modified cell-wall precursors for the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. Transglycosylase is responsible for the polymerization of the peptidoglycan, and the penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2) plays a major role in the polymerization among several transglycosylases of wild-type S. aureus. However, it is unclear whether VRSA processes the depsipeptide-containing peptidoglycan precursor by using PBP2. Here, we describe the total synthesis of depsi-lipid I, a cell-wall precursor of VRSA. By using this chemistry, we prepared a depsi-lipid II analogue as substrate for a cell-free transglycosylation system. The reconstituted system revealed that the PBP2 of S. aureus is able to process a depsi-lipid II intermediate as efficiently as its normal substrate. Moreover, the system was successfully used to demonstrate the difference in the mode of action of the two antibiotics moenomycin and vancomycin.
Keywords: antibiotics; enzymes; lipids; peptides; vancomycin.
© 2013 The Authors. Published by Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. This is an open access article under the terms of Creative Commons the Attribution Non‐Commercial NoDerivs License, which permits use and distribution in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited, the use is non‐commercial and no modifications or adaptations are made.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activated cell-wall synthesis is associated with vancomycin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains Mu3 and Mu50.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998 Aug;42(2):199-209. doi: 10.1093/jac/42.2.199. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998. PMID: 9738837
-
Moenomycin-resistance is associated with vancomycin-intermediate susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(12):927-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03466.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14695442
-
Katanosin B and plusbacin A(3), inhibitors of peptidoglycan synthesis in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Jun;45(6):1823-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1823-1827.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11353632 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a new model of antibiotic resistance.Lancet Infect Dis. 2001 Oct;1(3):147-55. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(01)00091-3. Lancet Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11871491 Review.
-
Inhibition of transglycosylation involved in bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis.Curr Med Chem. 2000 Aug;7(8):801-20. doi: 10.2174/0929867003374651. Curr Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 10828288 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the mode of action of cell wall-inhibiting antibiotics using metabolic labeling of growing peptidoglycan in Streptococcus pyogenes.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 25;7(1):1129. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01267-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28442740 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile synthesis of pathogen specific bacterial cell wall building blocks.RSC Adv. 2022 May 18;12(24):15046-15069. doi: 10.1039/d2ra01915a. eCollection 2022 May 17. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35702425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noble W, Virani Z, Cree R. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992;93:195–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

