ATR phosphorylates SMARCAL1 to prevent replication fork collapse
- PMID: 23873943
- PMCID: PMC3731549
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.214080.113
ATR phosphorylates SMARCAL1 to prevent replication fork collapse
Abstract
The DNA damage response kinase ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) coordinates much of the cellular response to replication stress. The exact mechanisms by which ATR regulates DNA synthesis in conditions of replication stress are largely unknown, but this activity is critical for the viability and proliferation of cancer cells, making ATR a potential therapeutic target. Here we use selective ATR inhibitors to demonstrate that acute inhibition of ATR kinase activity yields rapid cell lethality, disrupts the timing of replication initiation, slows replication elongation, and induces fork collapse. We define the mechanism of this fork collapse, which includes SLX4-dependent cleavage yielding double-strand breaks and CtIP-dependent resection generating excess single-stranded template and nascent DNA strands. Our data suggest that the DNA substrates of these nucleases are generated at least in part by the SMARCAL1 DNA translocase. Properly regulated SMARCAL1 promotes stalled fork repair and restart; however, unregulated SMARCAL1 contributes to fork collapse when ATR is inactivated in both mammalian and Xenopus systems. ATR phosphorylates SMARCAL1 on S652, thereby limiting its fork regression activities and preventing aberrant fork processing. Thus, phosphorylation of SMARCAL1 is one mechanism by which ATR prevents fork collapse, promotes the completion of DNA replication, and maintains genome integrity.
Keywords: ATR; DNA damage response; DNA replication; HARP; SMARCAL1; cell cycle checkpoint.
Figures


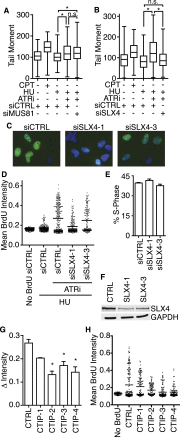
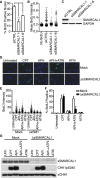

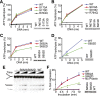
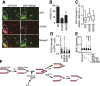
Comment in
-
Fork reversal, too much of a good thing.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(7):1049-50. doi: 10.4161/cc.28212. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24553113 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boerkoel CF, Takashima H, John J, Yan J, Stankiewicz P, Rosenbarker L, Andre JL, Bogdanovic R, Burguet A, Cockfield S, et al. 2002. Mutant chromatin remodeling protein SMARCAL1 causes Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia. Nat Genet 30: 215–220 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA09582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007028/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA136933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027485/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA171586-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA171586/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA090625/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES016486/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES016486/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA102792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
