The RNA-binding proteins FMR1, rasputin and caprin act together with the UBA protein lingerer to restrict tissue growth in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 23874212
- PMCID: PMC3708825
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003598
The RNA-binding proteins FMR1, rasputin and caprin act together with the UBA protein lingerer to restrict tissue growth in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
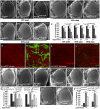
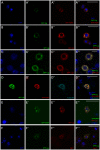
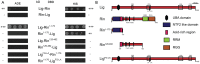
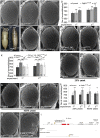
Appropriate expression of growth-regulatory genes is essential to ensure normal animal development and to prevent diseases like cancer. Gene regulation at the levels of transcription and translational initiation mediated by the Hippo and Insulin signaling pathways and by the TORC1 complex, respectively, has been well documented. Whether translational control mediated by RNA-binding proteins contributes to the regulation of cellular growth is less clear. Here, we identify Lingerer (Lig), an UBA domain-containing protein, as growth suppressor that associates with the RNA-binding proteins Fragile X mental retardation protein 1 (FMR1) and Caprin (Capr) and directly interacts with and regulates the RNA-binding protein Rasputin (Rin) in Drosophila melanogaster. lig mutant organs overgrow due to increased proliferation, and a reporter for the JAK/STAT signaling pathway is upregulated in a lig mutant situation. rin, Capr or FMR1 in combination as double mutants, but not the respective single mutants, display lig like phenotypes, implicating a redundant function of Rin, Capr and FMR1 in growth control in epithelial tissues. Thus, Lig regulates cell proliferation during development in concert with Rin, Capr and FMR1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

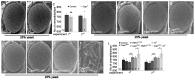
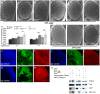
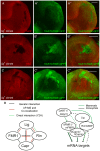
References
-
- Lypowy J, Chen I-Y, Abdellatif M (2005) An alliance between Ras GTPase-activating protein, filamin C, and Ras GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein regulates myocyte growth. J Biol Chem 280: 25717–25728. - PubMed
-
- Solomon S, Xu Y, Wang B, David MD, Schubert P, et al. (2007) Distinct structural features of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol 27: 2324–2342. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

