Reaching mothers and babies with early postnatal home visits: the implementation realities of achieving high coverage in large-scale programs
- PMID: 23874816
- PMCID: PMC3714261
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068930
Reaching mothers and babies with early postnatal home visits: the implementation realities of achieving high coverage in large-scale programs
Abstract
Background: Nearly half of births in low-income countries occur without a skilled attendant, and even fewer mothers and babies have postnatal contact with providers who can deliver preventive or curative services that save lives. Community-based maternal and newborn care programs with postnatal home visits have been tested in Bangladesh, Malawi, and Nepal. This paper examines coverage and content of home visits in pilot areas and factors associated with receipt of postnatal visits.
Methods: Using data from cross-sectional surveys of women with live births (Bangladesh 398, Malawi: 900, Nepal: 615), generalized linear models were used to assess the strength of association between three factors - receipt of home visits during pregnancy, birth place, birth notification - and receipt of home visits within three days after birth. Meta-analytic techniques were used to generate pooled relative risks for each factor adjusting for other independent variables, maternal age, and education.
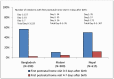
Findings: The proportion of mothers and newborns receiving home visits within three days after birth was 57% in Bangladesh, 11% in Malawi, and 50% in Nepal. Mothers and newborns were more likely to receive a postnatal home visit within three days if the mother received at least one home visit during pregnancy (OR2.18, CI1.46-3.25), the birth occurred outside a facility (OR1.48, CI1.28-1.73), and the mother reported a CHW was notified of the birth (OR2.66, CI1.40-5.08). Checking the cord was the most frequently reported action; most mothers reported at least one action for newborns.
Conclusions: Reaching mothers and babies with home visits during pregnancy and within three days after birth is achievable using existing community health systems if workers are available; linked to communities; and receive training, supplies, and supervision. In all settings, programs must evaluate what community delivery systems can handle and how to best utilize them to improve postnatal care access.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF WHO, World Bank, United Nations Population Division (2012) Levels and Trends of Child Mortality: Report 2012. New York: UNICEF.
-
- Lawn JE, Kinney MV, Black RE, Pitt C, Cousens S, et al. (2012) Newborn survival: a multi-country analysis of a decade of change. Health Policy Plan 27 Suppl 3iii6–28. - PubMed
-
- Darmstadt GL, Bhutta ZA, Cousens S, Adam T, Walker N, et al... (2005) Evidence-based, cost-effective interventions: how many newborn babies can we save? Lancet. 977–988. - PubMed
-
- Requejo J, Victora CG, Bryce J, Barros A, Berman P, et al... (2012) Countdown to 2015 - the 2012 Report: Building a Future for Women and Children. Washington, D.C.: World Health Organization and UNICEF 2012. 228 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

