Structural and functional characterisation of TesA - a novel lysophospholipase A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 23874889
- PMCID: PMC3715468
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069125
Structural and functional characterisation of TesA - a novel lysophospholipase A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
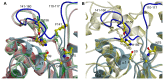
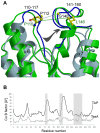
TesA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa belongs to the GDSL hydrolase family of serine esterases and lipases that possess a broad substrate- and regiospecificity. It shows high sequence homology to TAP, a multifunctional enzyme from Escherichia coli exhibiting thioesterase, lysophospholipase A, protease and arylesterase activities. Recently, we demonstrated high arylesterase activity for TesA, but only minor thioesterase and no protease activity. Here, we present a comparative analysis of TesA and TAP at the structural, biochemical and physiological levels. The crystal structure of TesA was determined at 1.9 Å and structural differences were identified, providing a possible explanation for the differences in substrate specificities. The comparison of TesA with other GDSL-hydrolase structures revealed that the flexibility of active-site loops significantly affects their substrate specificity. This assumption was tested using a rational approach: we have engineered the putative coenzyme A thioester binding site of E. coli TAP into TesA of P. aeruginosa by introducing mutations D17S and L162R. This TesA variant showed increased thioesterase activity comparable to that of TAP. TesA is the first lysophospholipase A described for the opportunistic human pathogen P. aeruginosa. The enzyme is localized in the periplasm and may exert important functions in the homeostasis of phospholipids or detoxification of lysophospholipids.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipase L1: consensus sequence blocks constitute the catalytic center of SGNH-hydrolases through a conserved hydrogen bond network.J Mol Biol. 2003 Jul 11;330(3):539-51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00637-5. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12842470
-
Functional role of a non-active site residue Trp(23) on the enzyme activity of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipase L(1).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Oct;1794(10):1467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.06.008. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19540368
-
Substrate specificities of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipase L1 are governed by its switch loop movement.Biochemistry. 2005 Feb 15;44(6):1971-9. doi: 10.1021/bi048109x. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15697222
-
Functional role of catalytic triad and oxyanion hole-forming residues on enzyme activity of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/phospholipase L1.Biochem J. 2006 Jul 1;397(1):69-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051645. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16515533 Free PMC article.
-
GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases.Prog Lipid Res. 2004 Nov;43(6):534-52. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2004.09.002. Prog Lipid Res. 2004. PMID: 15522763 Review.
Cited by
-
(Meta)genomic insights into the pathogenome of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans.Sci Rep. 2016 May 6;6:25527. doi: 10.1038/srep25527. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27151933 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Periplasmic Proteins of Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 and the Impact of Imipenem Exposure: A Proteomic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 13;20(14):3451. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143451. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337077 Free PMC article.
-
Marine picocyanobacterial PhnD1 shows specificity for various phosphorus sources but likely represents a constitutive inorganic phosphate transporter.ISME J. 2023 Jul;17(7):1040-1051. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01417-w. Epub 2023 Apr 22. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 37087502 Free PMC article.
-
Thioesterase enzyme families: Functions, structures, and mechanisms.Protein Sci. 2022 Mar;31(3):652-676. doi: 10.1002/pro.4263. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 34921469 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Lipolytic enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1329715. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1329715. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38357346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Upton C, Buckley JT (1995) A new family of lipolytic enzymes? Trends Biochem 20: 178-179. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(00)89002-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43: 534-552. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.09.002. PubMed: 15522763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heikinheimo P, Goldman A, Jeffries C, Ollis DL (1999) Of barn owls and bankers: a lush variety of alpha/beta hydrolases. Structure 7: R141-R146. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(99)80079-3. PubMed: 10404588. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ollis DL, Cheah E, Cygler M, Dijkstra B, Frolow F et al. (1992) The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng 5: 197-211. doi:10.1093/protein/5.3.197. PubMed: 1409539. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

