Extensive modulation of the transcription factor transcriptome during somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 23874927
- PMCID: PMC3714258
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069261
Extensive modulation of the transcription factor transcriptome during somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
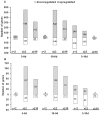
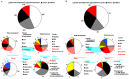
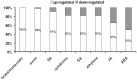
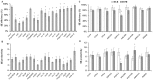
Molecular mechanisms controlling plant totipotency are largely unknown and studies on somatic embryogenesis (SE), the process through which already differentiated cells reverse their developmental program and become embryogenic, provide a unique means for deciphering molecular mechanisms controlling developmental plasticity of somatic cells. Among various factors essential for embryogenic transition of somatic cells transcription factors (TFs), crucial regulators of genetic programs, are believed to play a central role. Herein, we used quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to identify TF genes affected during SE induced by in vitro culture in Arabidopsis thaliana. Expression profiles of 1,880 TFs were evaluated in the highly embryogenic Col-0 accession and the non-embryogenic tanmei/emb2757 mutant. Our study revealed 729 TFs whose expression changes during the 10-days incubation period of SE; 141 TFs displayed distinct differences in expression patterns in embryogenic versus non-embryogenic cultures. The embryo-induction stage of SE occurring during the first 5 days of culture was associated with a robust and dramatic change of the TF transcriptome characterized by the drastic up-regulation of the expression of a great majority (over 80%) of the TFs active during embryogenic culture. In contrast to SE induction, the advanced stage of embryo formation showed attenuation and stabilization of transcript levels of many TFs. In total, 519 of the SE-modulated TFs were functionally annotated and transcripts related with plant development, phytohormones and stress responses were found to be most abundant. The involvement of selected TFs in SE was verified using T-DNA insertion lines and a significantly reduced embryogenic response was found for the majority of them. This study provides comprehensive data focused on the expression of TF genes during SE and suggests directions for further research on functional genomics of SE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Current Perspectives on the Auxin-Mediated Genetic Network that Controls the Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 16;21(4):1333. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041333. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression profiling of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR genes during somatic embryogenesis induction in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Jun;36(6):843-858. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2114-3. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28255787 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling reveals histone acetylation-regulated genes involved in somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 15;25(1):788. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10623-5. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39148037 Free PMC article.
-
AGL15 Controls the Embryogenic Reprogramming of Somatic Cells in Arabidopsis through the Histone Acetylation-Mediated Repression of the miRNA Biogenesis Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 14;21(18):6733. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186733. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32937992 Free PMC article.
-
Transduction of Signals during Somatic Embryogenesis.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;11(2):178. doi: 10.3390/plants11020178. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Perspectives on the Auxin-Mediated Genetic Network that Controls the Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 16;21(4):1333. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041333. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR156-SPL modules regulate induction of somatic embryogenesis in citrus callus.J Exp Bot. 2018 May 25;69(12):2979-2993. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery132. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29659948 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Auxin-Induced Somatic Embryogenesis in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 26;21(7):2307. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072307. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32225116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide transcriptome profiling of Carica papaya L. embryogenic callus.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2017 Apr;23(2):357-368. doi: 10.1007/s12298-017-0429-8. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2017. PMID: 28461724 Free PMC article.
-
miR393 contributes to the embryogenic transition induced in vitro in Arabidopsis via the modification of the tissue sensitivity to auxin treatment.Planta. 2016 Jul;244(1):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2505-7. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27040841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costa S, Shaw P (2007) „Open minded” cells: how cells can change fate. Trends Cell Biol 17: 101–106. - PubMed
-
- Dodeman VL, Ducreux G, Kreis M (1997) Zygotic embryogenesis versus somatic embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 48: 1493–1509.
-
- Long TA, Benfey PN (2006) Transcription factors and hormones: new insights into plant cell differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 710–714. - PubMed
-
- Riechmann JL, Ratcliffe OJ (2000) A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3: 423–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

