Fgf21 impairs adipocyte insulin sensitivity in mice fed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat ketogenic diet
- PMID: 23874946
- PMCID: PMC3706421
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069330
Fgf21 impairs adipocyte insulin sensitivity in mice fed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat ketogenic diet
Abstract
Background: A low-carbohydrate, high-fat ketogenic diet (KD) induces hepatic ketogenesis and is believed to affect energy metabolism in mice. As hepatic Fgf21 expression was markedly induced in mice fed KD, we examined the effects of KD feeding on metabolism and the roles of Fgf21 in metabolism in mice fed KD using Fgf21 knockout mice.
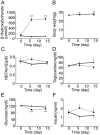
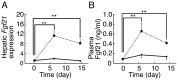
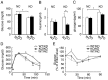
Methodology/principal findings: We examined C57BL/6 mice fed KD for 6 or 14 days. Blood β-hydroxybutyrate levels were greatly increased at 6 days, indicating that hepatic ketogenesis was induced effectively by KD feeding for 6 days. KD feeding for 6 and 14 days impaired glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, although it did not affect body weight, blood NEFA, and triglyceride levels. Hepatic Fgf21 expression and blood Fgf21 levels were markedly increased in mice fed KD for 6 days. Blood β-hydroxybutyrate levels in the knockout mice fed KD for 6 days were comparable to those in wild-type mice fed KD, indicating that Fgf21 is not required for ketogenesis. However, the impaired glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity caused by KD feeding were improved in the knockout mice. Insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation was significantly decreased in the white adipose tissue in wild-type mice fed KD compared with those fed normal chow, but not in the muscle and liver. Its phosphorylation in the white adipose tissue was significantly increased in the knockout mice fed KD compared with wild-type mice fed KD. In contrast, hepatic gluconeogenic gene expression in Fgf21 knockout mice fed KD was comparable to those in the wild-type mice fed KD.
Conclusions/significance: The present findings indicate that KD feeding impairs insulin sensitivity in mice due to insulin resistance in white adipose tissue. In addition, our findings indicate that Fgf21 induced to express by KD is a negative regulator of adipocyte insulin sensitivity in adaptation to a low-carbohydrate malnutritional state.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
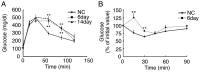



References
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM (2008) Functional evolutionary history of the mouse Fgf gene familiy. Dev. Dyn. 237: 18–27. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N (2000) Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1492: 203–206. - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Larsen P (2011) FGF21 reloaded: challenges of a rapidly growing field. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 22: 81–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

