sox4 and sox11 function during Xenopus laevis eye development
- PMID: 23874955
- PMCID: PMC3715537
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069372
sox4 and sox11 function during Xenopus laevis eye development
Abstract
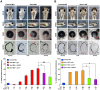
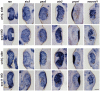
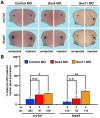
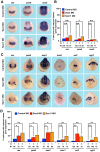
SoxC genes are involved in many developmental processes such as cardiac, lymphoid, and bone development. The SoxC gene family is represented by Sox4, Sox11, and Sox12. Loss of either Sox4 or Sox11 function is lethal during mouse embryogenesis. Here, we demonstrate that sox4 and sox11 are strongly expressed in the developing eye, heart as well as brain in Xenopus laevis. Morpholino oligonucleotide mediated knock-down approaches in anterior neural tissue revealed that interference with either Sox4 or Sox11 function affects eye development. A detailed analysis demonstrated strong effects on eye size and retinal lamination. Neural induction was unaffected upon Sox4 or Sox11 MO injection and early eye field differentiation and cell proliferation were only mildly affected. Depletion of both genes, however, led independently to a significant increase in cell apoptosis in the eye. In summary, Sox4 and Sox11 are required for Xenopus visual system development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Zuber ME, Gestri G, Viczian AS, Barsacchi G, Harris WA (2003) Specification of the vertebrate eye by a network of eye field transcription factors. Development 130: 5155–5167. - PubMed
-
- Chow RL, Lang RA (2001) Early eye development in vertebrates. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17: 255–296. - PubMed
-
- Kiefer JC (2007) Back to basics: Sox genes. Developmental Dynamics 236: 2356–2366. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126: 663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

