ERK positive feedback regulates a widespread network of tyrosine phosphorylation sites across canonical T cell signaling and actin cytoskeletal proteins in Jurkat T cells
- PMID: 23874979
- PMCID: PMC3714263
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069641
ERK positive feedback regulates a widespread network of tyrosine phosphorylation sites across canonical T cell signaling and actin cytoskeletal proteins in Jurkat T cells
Abstract
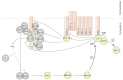
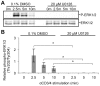
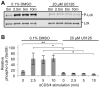
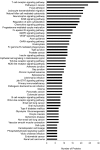
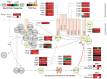
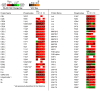
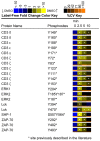
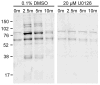
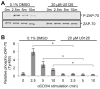
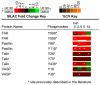
Competing positive and negative signaling feedback pathways play a critical role in tuning the sensitivity of T cell receptor activation by creating an ultrasensitive, bistable switch to selectively enhance responses to foreign ligands while suppressing signals from self peptides. In response to T cell receptor agonist engagement, ERK is activated to positively regulate T cell receptor signaling through phosphorylation of Ser(59) Lck. To obtain a wide-scale view of the role of ERK in propagating T cell receptor signaling, a quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of 322 tyrosine phosphorylation sites by mass spectrometry was performed on the human Jurkat T cell line in the presence of U0126, an inhibitor of ERK activation. Relative to controls, U0126-treated cells showed constitutive decreases in phosphorylation through a T cell receptor stimulation time course on tyrosine residues found on upstream signaling proteins (CD3 chains, Lck, ZAP-70), as well as downstream signaling proteins (VAV1, PLCγ1, Itk, NCK1). Additional constitutive decreases in phosphorylation were found on the majority of identified proteins implicated in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton pathway. Although the majority of identified sites on T cell receptor signaling proteins showed decreases in phosphorylation, Tyr(598) of ZAP-70 showed elevated phosphorylation in response to U0126 treatment, suggesting differential regulation of this site via ERK feedback. These findings shed new light on ERK's role in positive feedback in T cell receptor signaling and reveal novel signaling events that are regulated by this kinase, which may fine tune T cell receptor activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Acuto O, Di Bartolo V, Micheli F (2008) Tailoring T-cell receptor signals by proximal negative feedback mechanisms. Nat Rev Immunol 8: 699–712. - PubMed
-
- Palacios EH, Weiss A (2004) Function of the Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and activation. Oncogene 23: 7990–8000. - PubMed
-
- Au-Yeung BB, Deindl S, Hsu LY, Palacios EH, Levin SE, et al. (2009) The structure, regulation, and function of ZAP-70. Immunol Rev 228: 41–57. - PubMed
-
- Stefanova I, Hemmer B, Vergelli M, Martin R, Biddison WE, et al. (2003) TCR ligand discrimination is enforced by competing ERK positive and SHP-1 negative feedback pathways. Nat Immunol 4: 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Mueller DL (2003) Tuning the immune system: competing positive and negative feedback loops. Nat Immunol 4: 210–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

