Cloud-based uniform ChIP-Seq processing tools for modENCODE and ENCODE
- PMID: 23875683
- PMCID: PMC3734164
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-494
Cloud-based uniform ChIP-Seq processing tools for modENCODE and ENCODE
Abstract
Background: Funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the aim of the Model Organism ENCyclopedia of DNA Elements (modENCODE) project is to provide the biological research community with a comprehensive encyclopedia of functional genomic elements for both model organisms C. elegans (worm) and D. melanogaster (fly). With a total size of just under 10 terabytes of data collected and released to the public, one of the challenges faced by researchers is to extract biologically meaningful knowledge from this large data set. While the basic quality control, pre-processing, and analysis of the data has already been performed by members of the modENCODE consortium, many researchers will wish to reinterpret the data set using modifications and enhancements of the original protocols, or combine modENCODE data with other data sets. Unfortunately this can be a time consuming and logistically challenging proposition.
Results: In recognition of this challenge, the modENCODE DCC has released uniform computing resources for analyzing modENCODE data on Galaxy (https://github.com/modENCODE-DCC/Galaxy), on the public Amazon Cloud (http://aws.amazon.com), and on the private Bionimbus Cloud for genomic research (http://www.bionimbus.org). In particular, we have released Galaxy workflows for interpreting ChIP-seq data which use the same quality control (QC) and peak calling standards adopted by the modENCODE and ENCODE communities. For convenience of use, we have created Amazon and Bionimbus Cloud machine images containing Galaxy along with all the modENCODE data, software and other dependencies.
Conclusions: Using these resources provides a framework for running consistent and reproducible analyses on modENCODE data, ultimately allowing researchers to use more of their time using modENCODE data, and less time moving it around.
Figures
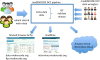


References
-
- Celniker SE, Dillon LA, Gerstein MB, Gunsalus KC, Henikoff S, Karpen GH, Kellis M, Lai EC, Lieb JD, MacAlpine DM, Micklem G, Piano F, Snyder M, Stein L, White KP, Waterston RH. modENCODE Consortium. Unlocking the secrets of the genome. Nature. 2009;459(7249):927–930. doi: 10.1038/459927a. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Washington NL, Stinson EO, Perry MD, Ruzanov P, Contrino S, Smith R, Zha Z, Lyne R, Carr A, Lloyd P, Kephart E, McKay SJ, Micklem G, Stein LD, Lewis SE. The modENCODE Data Coordination Center: lessons in harvesting comprehensive experimental detail. Database. 2011;2011:bar023. doi: 10.1093/database/bar023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- modENCODE Galaxy GitHub. https://github.com/modENCODE-DCC/Galaxy.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

