Growing up in the genomic era: implications of whole-genome sequencing for children, families, and pediatric practice
- PMID: 23875800
- PMCID: PMC4159555
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153425
Growing up in the genomic era: implications of whole-genome sequencing for children, families, and pediatric practice
Abstract
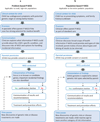
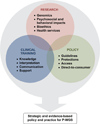
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) has advanced to a point where it is beginning to be integrated into pediatric practice. With little consensus on how to maximize the benefits of WGS for children, there is a growing need for focused efforts that connect researchers, clinicians, and families to chart a path forward. To illustrate relevant concerns, two contrasting applications of pediatric WGS are explored: clinical use with children who have undiagnosed conditions, and population-based screening. Specific challenges for health care services, policy development, and the well-being of children are discussed in light of current research. In the interest of ensuring evidence-based pediatric WGS, strategies are identified for advancing our understanding of what it means for children to grow up with WGS results guiding their health care.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander D, van Dyck PC. A vision of the future of newborn screening. Pediatrics. 2006;117:S350–S354. - PubMed
-
- Almond B. Genetic profiling of newborns: ethical and social issues. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Berg JS, Khoury MJ, Evans JP. Deploying whole genome sequencing in clinical practice and public health: meeting the challenge one bin at a time. Genet. Med. 2011;13:499–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

