Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipid ameliorates insulin resistance and lipid metabolism in diet-induced-obese mice
- PMID: 23876229
- PMCID: PMC3728066
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-109
Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipid ameliorates insulin resistance and lipid metabolism in diet-induced-obese mice
Abstract
Background: Over the past two decades, a striking increase in the number of people with metabolic syndrome (MS) has taken place worldwide. With the elevated risk of not only diabetes but also cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, there is urgent need for strategies to prevent this emerging global epidemic. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effects of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipid (EPA-PL) on metabolic disorders.
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mice (n = 7) were fed one of the following 4 diets for a period of 4 weeks: 1) a modified AIN-96G diet with 5% corn oil (control diet); 2) a high fat (20%, wt/wt) and high fructose (20%, wt/wt) diet (HF diet); 3) the HF diet containing 1% SOY-PL (SOY-PL diet); 4) the HF diet containing 1% EPA-PL (EPA-PL diet). The oral glucose tolerance test was performed. Plasma TG, TC, glucose, NEFA, insulin, leptin, adiponectin, TNF-α and IL-6 levels were assessed. In addition, hepatic lipid levels, lipogenic, and lipidolytic enzyme activities and gene expressions were evaluated.
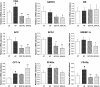
Results: Both EPA-PL and SOY-PL significantly inhibited body weight gain and white adipose tissue accumulation, alleviated glucose intolerance, and lowered both serum fasting glucose and NEFA levels substantially. Only EPA-PL significantly reduced serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels, and increased serum adiponectin level. EPA-PL was more effective in reducing hepatic and serum TG and TC levels than SOY-PL. Both EPA-PL and SOY-PL reduced the activities of hepatic lipogenic enzymes, such as FAS and G6PDH, but only EPA-PL significantly increased CPT, peroxisomal β-oxidation enzymes activities and CPT-1a mRNA level. Alterations of hepatic lipogenic gene expressions, such as FAS, G6PDH, ACC, SCD-1 and SREBP-1c were consistent with changes in related enzyme activities.
Conclusions: According to our study, EPA-PL supplementation was efficacious in suppressing body fat accumulation, and alleviating insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis by modulating the secretion of adipocytokines and inflammatory cytokines, suppression of SREBP-1c mediated lipogenesis and enhancement of fatty acid β-oxidation. These results demonstrate that EPA-PL is a novel beneficial food component for the prevention and improvement of metabolic disorders.
Figures
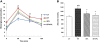
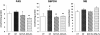
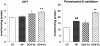
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effect of sea cucumber saponins and EPA-enriched phospholipids on insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Food Funct. 2019 Jul 17;10(7):3955-3964. doi: 10.1039/c9fo01147a. Food Funct. 2019. PMID: 31199413
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents and reverses insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice via modulation of adipose tissue inflammation.J Nutr. 2010 Nov;140(11):1915-22. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.125732. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20861209
-
Medium-chain triglyceride ameliorates insulin resistance and inflammation in high fat diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Apr;55(3):931-40. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0907-0. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25911003
-
Pathway-selective insulin resistance and metabolic disease: the importance of nutrient flux.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 25;289(30):20462-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.576355. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24907277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Mechanisms by Which Hydroxyeicosapentaenoic Acids Regulate Glucose Homeostasis in Obesity.Adv Nutr. 2022 Dec 22;13(6):2316-2328. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmac073. Adv Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35709423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effect of eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids and sea cucumber saponin on orotic acid-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats.R Soc Open Sci. 2018 Jul 11;5(7):172182. doi: 10.1098/rsos.172182. eCollection 2018 Jul. R Soc Open Sci. 2018. PMID: 30109054 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent hepatic alterations induced by a high-fat high-fructose diet.Inflamm Res. 2019 May;68(5):359-368. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01223-1. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 30874869
-
Effects of Dietary Fatty Acids in Pancreatic Beta Cell Metabolism, Implications in Homeostasis.Nutrients. 2018 Mar 22;10(4):393. doi: 10.3390/nu10040393. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29565831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
12-lipoxygenase promotes obesity-induced oxidative stress in pancreatic islets.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Oct 1;34(19):3735-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00157-14. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25071151 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lysophospholipid on Growth Performance, Hepatopancreas Health, and Intestinal Microbiome of Litopenaeus vannamei in Low-Fishmeal Diet.Aquac Nutr. 2024 Dec 19;2024:8883996. doi: 10.1155/anu/8883996. eCollection 2024. Aquac Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39735179 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

