Piceatannol suppresses the metastatic potential of MCF10A human breast epithelial cells harboring mutated H-ras by inhibiting MMP-2 expression
- PMID: 23877152
- PMCID: PMC3812238
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1449
Piceatannol suppresses the metastatic potential of MCF10A human breast epithelial cells harboring mutated H-ras by inhibiting MMP-2 expression
Abstract
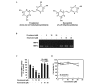
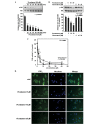
Metastasis is one of the most threatening features of the oncogenic process and the main cause of cancer-related mortality. Several studies have demonstrated that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are critical for tumor invasion and metastasis. Resveratrol (3,5,4'-trihydroxystilbene), a phenolic compound of red wine, has been reported to be a natural chemopreventive agent. However, the cancer preventive effects of piceatannol (3,5,3',4'-tetrahydroxystilbene), a metabolite of resveratrol and the underlying molecular mechanisms have not yet been fully elucidated. In this study, we report that piceatannol inhi-bits H-ras-induced MMP-2 activity and the invasive phenotype of MCF10A human breast epithelial cells harboring mutated H-ras (H-ras MCF10A cells) more effectively than resveratrol. Piceatannol attenuated the H-ras-induced phosphorylation of Akt in a time- and dose-dependent manner, whereas resveratrol, at the same concentrations, did not exert an inhibitory effect. In vitro kinase assays demonstrated that piceatannol significantly inhibited phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity and suppressed phospha-tidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) expression in the H-ras MCF10A cells. Ex vivo pull-down assays revealed that piceatannol directly bound to PI3K, inhibiting PI3K activity. Data from molecular docking suggested that piceatannol is a more tight-binding inhibitor than resveratrol due to the additional hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl group and the backbone amide group of Val882 in the ATP-binding pocket of PI3K.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quercetin suppresses invasion and migration of H-Ras-transformed MCF10A human epithelial cells by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Food Chem. 2014 Jan 1;142:66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24001813
-
Piceatannol suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through the inhibition of MMP-9: involvement of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Apr 25;60(16):4083-9. doi: 10.1021/jf205171g. Epub 2012 Apr 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22480333
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is a novel target of piceatannol for inhibiting PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration in human aortic smooth muscle cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Mar 1;85(4):836-44. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp359. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 19887493
-
Biological activity of piceatannol: leaving the shadow of resveratrol.Mutat Res. 2012 Jan-Mar;750(1):60-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.11.001. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 22108298 Review.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of naturally occurring piceatannol in non-communicable diseases.Biofactors. 2024 Mar-Apr;50(2):232-249. doi: 10.1002/biof.2009. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 37702264 Review.
Cited by
-
Albumin Nano-Encapsulation of Piceatannol Enhances Its Anticancer Potential in Colon Cancer Via Downregulation of Nuclear p65 and HIF-1α.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 1;12(1):113. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010113. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31906321 Free PMC article.
-
Piceatannol induced apoptosis through up-regulation of microRNA-181a in melanoma cells.Biol Res. 2017 Oct 17;50(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40659-017-0141-8. Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 29041990 Free PMC article.
-
Piceatannol suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulation of the microRNA‑21/phosphatase and tensin homolog/protein kinase B signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):3985-3993. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11484. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32901863 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of SIRTs activator resveratrol and its derivatives in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1390907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1390907. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38962006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin decreases breast cancer metastasis by modulating Rho-associated kinase protein-1 expression.J Pineal Res. 2016 Jan;60(1):3-15. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12270. Epub 2015 Oct 20. J Pineal Res. 2016. PMID: 26292662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sporn MB. The war on cancer. Lancet. 1996;347:1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6130–6138. - PubMed
-
- Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991;64:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, et al. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature. 1994;370:61–65. - PubMed
-
- McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: multifunctional contributors to tumor progression. Mol Med Today. 2000;6:149–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

