Graph-based modeling of tandem repeats improves global multiple sequence alignment
- PMID: 23877246
- PMCID: PMC3783189
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt628
Graph-based modeling of tandem repeats improves global multiple sequence alignment
Abstract
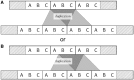
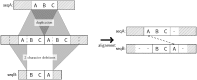
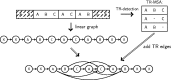
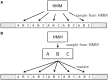
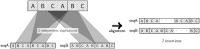
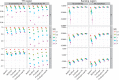
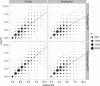
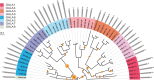
Tandem repeats (TRs) are often present in proteins with crucial functions, responsible for resistance, pathogenicity and associated with infectious or neurodegenerative diseases. This motivates numerous studies of TRs and their evolution, requiring accurate multiple sequence alignment. TRs may be lost or inserted at any position of a TR region by replication slippage or recombination, but current methods assume fixed unit boundaries, and yet are of high complexity. We present a new global graph-based alignment method that does not restrict TR unit indels by unit boundaries. TR indels are modeled separately and penalized using the phylogeny-aware alignment algorithm. This ensures enhanced accuracy of reconstructed alignments, disentangling TRs and measuring indel events and rates in a biologically meaningful way. Our method detects not only duplication events but also all changes in TR regions owing to recombination, strand slippage and other events inserting or deleting TR units. We evaluate our method by simulation incorporating TR evolution, by either sampling TRs from a profile hidden Markov model or by mimicking strand slippage with duplications. The new method is illustrated on a family of type III effectors, a pathogenicity determinant in agriculturally important bacteria Ralstonia solanacearum. We show that TR indel rate variation contributes to the diversification of this protein family.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deep conservation of human protein tandem repeats within the eukaryotes.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 May;31(5):1132-48. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu062. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24497029 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical approaches to detecting and analyzing tandem repeats in genomic sequences.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Mar 17;3:31. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00031. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25853125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution and function of protein tandem repeats in plants.New Phytol. 2015 Apr;206(1):397-410. doi: 10.1111/nph.13184. Epub 2014 Nov 24. New Phytol. 2015. PMID: 25420631
-
Please Mind the Gap: Indel-Aware Parsimony for Fast and Accurate Ancestral Sequence Reconstruction and Multiple Sequence Alignment Including Long Indels.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Jul 3;41(7):msae109. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae109. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38842253 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing genomic technologies and clinical awareness accelerates discovery of disease-associated tandem repeat sequences.Genome Res. 2022 Jan;32(1):1-27. doi: 10.1101/gr.269530.120. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 34965938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tandem repeats lead to sequence assembly errors and impose multi-level challenges for genome and protein databases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 2;47(21):10994-11006. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz841. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31584084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A depauperate immune repertoire precedes evolution of sociality in bees.Genome Biol. 2015 Apr 24;16(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0628-y. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 25908406 Free PMC article.
-
Maximum-Likelihood Tree Estimation Using Codon Substitution Models with Multiple Partitions.Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Aug;32(8):2208-16. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv097. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25911229 Free PMC article.
-
A New Census of Protein Tandem Repeats and Their Relationship with Intrinsic Disorder.Genes (Basel). 2020 Apr 9;11(4):407. doi: 10.3390/genes11040407. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32283633 Free PMC article.
-
Repertoire, unified nomenclature and evolution of the Type III effector gene set in the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex.BMC Genomics. 2013 Dec 6;14:859. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-859. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24314259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Löytynoja A, Goldman N. Phylogeny-aware gap placement prevents errors in sequence alignment and evolutionary analysis. Science. 2008;320:16325. - PubMed
-
- Anisimova M, Cannarozzi G, Liberles DA. Finding the balance between the mathematical and biological optima in multiple sequence alignment. Trends Evol. Biol. 2010;2:e7.
-
- Sammeth M, Heringa J. Global multiple-sequence alignment with repeats. Proteins. 2006;64:263274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

