Interaction of smoothened with integrin-linked kinase in primary cilia mediates Hedgehog signalling
- PMID: 23877428
- PMCID: PMC3790053
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2013.110
Interaction of smoothened with integrin-linked kinase in primary cilia mediates Hedgehog signalling
Erratum in
- EMBO Rep. 2013 Oct;14(10):945. Martellotto, Luciano G [corrected to Martelotto, Luciano G]
Abstract
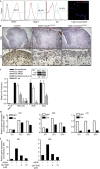
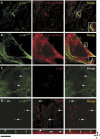
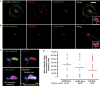
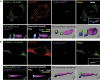
Here we report that ILK localizes in the mouse primary cilium, a sensory organelle required for signalling by the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of ILK blocks ciliary accumulation of the Hh pathway effector smoothened (Smo) and suppresses the induction of Gli transcription factor mRNAs by SHh. Conditional deletion of ILK or Smo also inhibits SHh-driven activation of Gli2 in the embryonic mouse cerebellum. ILK regulation of Hh signalling probably requires the physical interaction of ILK and Smo in the cilium, and we also show selective cilia-associated interaction of ILK with β-arrestin, a known mediator of Smo-dependent signalling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Integrin-linked kinase in ciliary Hedgehog signaling.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(6):871-2. doi: 10.4161/cc.28188. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24552818 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Bifurcating action of Smoothened in Hedgehog signaling is mediated by Dlg5.Genes Dev. 2015 Feb 1;29(3):262-76. doi: 10.1101/gad.252676.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25644602 Free PMC article.
-
The intrahepatic signalling niche of hedgehog is defined by primary cilia positive cells during chronic liver injury.J Hepatol. 2014 Jan;60(1):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.012. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23978713
-
Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 22;106(51):21666-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912180106. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19996169 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling pathway: a novel model and molecular mechanisms of signal transduction.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1317-32. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2127-4. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26762301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Smoothened Regulation in Hedgehog Signaling.Cells. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):2138. doi: 10.3390/cells10082138. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat exerts its neurotoxic effects by downregulating Sonic hedgehog signaling.J Neurovirol. 2022 Apr;28(2):305-311. doi: 10.1007/s13365-022-01061-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Neurovirol. 2022. PMID: 35181862 Free PMC article.
-
Ins and outs of GPCR signaling in primary cilia.EMBO Rep. 2015 Sep;16(9):1099-113. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540530. Epub 2015 Aug 21. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 26297609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary Cilia and Calcium Signaling Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 26;21(19):7109. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197109. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32993148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymosin beta-4 regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells via hedgehog signaling.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 19;7(1):3815. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03782-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28630423 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hedgehog signaling by ubiquitination.Front Biol (Beijing). 2015 Jun;10(3):203-220. doi: 10.1007/s11515-015-1343-5. Front Biol (Beijing). 2015. PMID: 26366162 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

