Improvement of the pharmacokinetics and in vivo antibacterial efficacy of a novel type IIa topoisomerase inhibitor by formulation in liposomes
- PMID: 23877679
- PMCID: PMC3811447
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00163-13
Improvement of the pharmacokinetics and in vivo antibacterial efficacy of a novel type IIa topoisomerase inhibitor by formulation in liposomes
Abstract
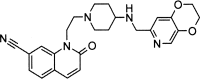
Several useful properties of liposome-based formulations of various existing antibacterial drugs have been reported. These properties include lower MICs, improved pharmacokinetics, lower toxicity, selective distribution to infected tissues, and enhanced in vivo efficacy. Here we report in vivo studies of a liposomal formulation of a member of a novel class of antibacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors, others of which have progressed to early phases of clinical trials. The free (i.e., nonliposomal) compound has broad-spectrum MICs but suboptimal pharmacokinetics in rats and mice, characterized by a high volume of distribution and rapid clearance. The liposomal formulation of the compound had essentially unchanged MICs but greatly reduced volume of distribution and clearance in rats and mice. In an in vivo mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus infection of one thigh, the liposomal compound localized preferentially to the infected thigh, whereas the free compound showed no preference for the infected versus the uninfected thigh. Most importantly, the liposomal compound had enhanced efficacy at clearing the infection compared with the free compound. Delivery of this class of compounds as liposomal formulations may offer clinical advantages compared with free compounds.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Responding to the challenge of untreatable gonorrhea: ETX0914, a first-in-class agent with a distinct mechanism-of-action against bacterial Type II topoisomerases.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 14;5:11827. doi: 10.1038/srep11827. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26168713 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimization of pyrrolamide topoisomerase II inhibitors toward identification of an antibacterial clinical candidate (AZD5099).J Med Chem. 2014 Jul 24;57(14):6060-82. doi: 10.1021/jm500462x. Epub 2014 Jul 8. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24959892
-
Structure activity relationship of C-2 ether substituted 1,5-naphthyridine analogs of oxabicyclooctane-linked novel bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors as broad-spectrum antibacterial agents (Part-5).Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Sep 1;25(17):3630-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.061. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26152426
-
Recent advancements in the medicinal chemistry of bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104266. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104266. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142421 Review.
-
Clinical development of liposome-based drugs: formulation, characterization, and therapeutic efficacy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:49-60. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26766. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22275822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The bactericidal effect of liposomal vancomycin as a topical combating system against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin wound infection in mice.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2019 Dec 26;33:153. doi: 10.34171/mjiri.33.153. eCollection 2019. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2019. PMID: 32280659 Free PMC article.
-
Time for a change: addressing R&D and commercialization challenges for antibacterials.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 5;370(1670):20140086. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0086. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25918443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bax BD, Chan PF, Eggleston DS, Fosberry A, Gentry DR, Gorrec F, Giordano I, Hann MM, Hennessy A, Hibbs M, Huang J, Jones E, Jones J, Koretke Brown K, Lewis CJ, May EW, Saunders MR, Singh O, Spitzfaden CE, Shen C, Shillings A, Theobald AJ, Wohlkonig A, Pearson ND, Gwynn MN. 2010. Type IIA topoisomerase inhibition by a new class of antibacterial agents. Nature 466:935–940 - PubMed
-
- Geng B, Comita-Prevoir J, Eyermann CJ, Reck F, Fisher S. 2011. Exploring left-hand-side substitutions in the benzoxazinone series of 4-amino-piperidine bacterial type IIa topoisomerase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21:5432–5435 - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AB, Andrews B. 2012. Allosteric inhibition of the DNA-dependent ATPase activity of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase by a representative of a novel class of inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 84:900–904 - PubMed
-
- Fenske DB, Cullis PR. 2005. Entrapment of small molecules and nucleic acid-based drugs in liposomes. Methods Enzymol. 391:7–40 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

