Standing balance tests for screening people with vestibular impairments
- PMID: 23877965
- PMCID: PMC3841227
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.24314
Standing balance tests for screening people with vestibular impairments
Abstract
Objectives/hypothesis: To improve the test standards for a version of the Romberg test and to determine whether measuring kinematic variables improved its utility for screening.
Study design: Healthy controls and patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, postoperative acoustic neuroma resection, and chronic peripheral unilateral weakness were compared.
Methods: Subjects wore Bluetooth-enabled inertial motion units while standing on the floor or medium-density, compliant foam, with eyes open or closed, with head still or moving in pitch or yaw. Dependent measures were time to perform each test condition, number of head movements made, and kinematic variables.
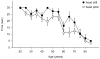
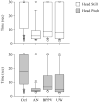
Results: Patients and controls did not differ significantly with eyes open or with eyes closed while on the floor. With eyes closed, on foam, some significant differences were found between patients and controls, especially for subjects older than 59 years. Head movement conditions were more challenging than with the head still. Significantly fewer patients than controls could make enough head movements to obtain kinematic measures. Kinematics indicated that lateral balance control is significantly reduced in these patients compared to controls. Receiver operator characteristics and sensitivity/specificity analyses showed moderately good differences with older subjects.
Conclusions: Tests on foam with eyes closed, with head still or moving, may be useful as part of a screening battery for vestibular impairments, especially for older people.
Level of evidence: 3b.
Keywords: Balance testing; Romberg; screening; vestibular testing.
Copyright © 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lanska DJ. The Romberg sign and early instruments for measuring postural sway. Semin Neurol. 2002;22:409–18. - PubMed
-
- Nashner LM. Computerized dynamic posturography: clinical applications. In: Jacobson GP, Newman CW, Kartush JM, editors. Handbook of Balance Function Testing. St. Louis, MO: Mosby-Year Book; 1993. pp. 308–34.
-
- Analytic and Reporting Guidelines: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) National Center for Health Statistics Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2006.
-
- Shumway-Cook A, Horak FB. Assessing the influence of sensory interaction on balance. Phys Ther. 1986;66:1548–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

