Dynamic metabolic imaging of hyperpolarized [2-(13) C]pyruvate using spiral chemical shift imaging with alternating spectral band excitation
- PMID: 23878057
- PMCID: PMC3849119
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.24871
Dynamic metabolic imaging of hyperpolarized [2-(13) C]pyruvate using spiral chemical shift imaging with alternating spectral band excitation
Abstract
Purpose: In contrast to [1-(13) C]pyruvate, hyperpolarized [2-(13) C]pyruvate permits the ability to follow the (13) C label beyond flux through pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and investigate the incorporation of acetyl-coenzyme A into different metabolic pathways. However, chemical shift imaging (CSI) with [2-(13) C]pyruvate is challenging owing to the large spectral dispersion of the resonances, which also leads to severe chemical shift displacement artifacts for slice-selective acquisitions.
Methods: This study introduces a sequence for three-dimensional CSI of [2-(13) C]pyruvate using spectrally selective excitation of limited frequency bands containing a subset of metabolites. Dynamic CSI data were acquired alternately from multiple frequency bands in phantoms for sequence testing and in vivo in rat heart.
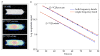
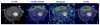
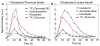
Results: Phantom experiments verified the radiofrequency pulse design and demonstrated that the signal behavior of each group of resonances was unaffected by excitation of the other frequency bands. Dynamic three-dimensional (13) C CSI data demonstrated the sequence capability to image pyruvate, lactate, acetylcarnitine, glutamate, and acetoacetate, enabling the analysis of organ-specific spectra and metabolite time courses.
Conclusions: The presented method allows CSI of widely separated resonances without chemical shift displacement artifact, acquiring multiple frequency bands alternately to obtain dynamic time-course information. This approach enables robust imaging of downstream metabolic products of acetyl-coenzyme A with hyperpolarized [2-(13) C]pyruvate.
Keywords: [2-13C]pyruvate; dynamic metabolic imaging; hyperpolarized 13C; spiral CSI.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
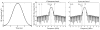
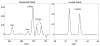
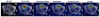
References
-
- Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Brindle K, Chekmenev EY, Comment A, Cunningham CH, Deberardinis RJ, Green GG, Leach MO, Rajan SS, Rizi RR, Ross BD, Warren WS, Malloy CR. Analysis of cancer metabolism by imaging hyperpolarized nuclei: prospects for translation to clinical research. Neoplasia. 2011;13(2):81–97. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brindle KM, Bohndiek SE, Gallagher FA, Kettunen MI. Tumor imaging using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 2011;66(2):505–519. - PubMed
-
- Golman K, Zandt RI, Lerche M, Pehrson R, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH. Metabolic imaging by hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo tumor diagnosis. Cancer Res. 2006;66(22):10855–10860. - PubMed
-
- Kohler SJ, Yen Y, Wolber J, Chen AP, Albers MJ, Bok R, Zhang V, Tropp J, Nelson S, Vigneron DB, Kurhanewicz J, Hurd RE. In vivo 13carbon metabolic imaging at 3T with hyperpolarized 13C-1-pyruvate. Magn Reson Med. 58(1):65–69. 207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

