Evaluation of a nanoemulsion formulation strategy for oral bioavailability enhancement of danazol in rats and dogs
- PMID: 23878097
- PMCID: PMC3773250
- DOI: 10.1002/jps.23667
Evaluation of a nanoemulsion formulation strategy for oral bioavailability enhancement of danazol in rats and dogs
Abstract
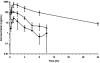
The objective of this study was to determine whether nanoemulsion formulations constitute a viable strategy to improve the oral bioavailability of danazol, a compound whose poor aqueous solubility limits its oral bioavailability. Danazol-containing oil-in-water nanoemulsions (NE) with and without cosurfactants stearylamine (SA) and deoxycholic acid (DCA) were prepared and characterized. Nanoemulsion droplets size ranging from 238 to 344 nm and with surface charges of -24.8 mV (NE), -26.5 mV (NE-DCA), and +27.8 mV (NE-SA) were reproducibly obtained. Oral bioavailability of danazol in nanoemulsions was compared with other vehicles such as PEG400, 1% methylcellulose (MC) in water (1% MC), Labrafil, and a Labrafil/Tween 80 (9:1) mixture, after intragastric administration to rats and after oral administration of NE-SA, a Labrafil solution, or a Danocrine® tablet to dogs. The absolute bioavailability of danazol was 0.6% (PEG400), 1.2% (1% MC), 6.0% (Labrafil), 7.5% (Labrafil/Tween80), 8.1% (NE-DCA), 14.8% (NE), and 17.4% (NE-SA) in rats, and 0.24% (Danocrine), 6.2% (Labrafil), and 58.7% (NE-SA) in dogs. Overall, danazol bioavailability in any nanoemulsion was higher than any other formulation. Danazol bioavailability from NE and NE-SA was 1.8- to 2.2-fold higher than NE-DCA nanoemulsion and could be due to significant difference in droplet size.
Keywords: absorption; bioavailability; danazol; hepatic clearance; nanoemulsion; particle size; stearylamine; surfactants.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. and the American Pharmacists Association.
Figures



References
-
- Gao P, Rush BD, Pfund WP, Huang T, Bauer JM, Morozowich W, Kuo M, Hageman MJ. Development of a supersaturable SEDDS (S-SEDDS) formulation of paclitaxel with improved oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92:2386–2398. - PubMed
-
- Ansell SM, Johnstone SA, Tardi PG, Lo L, Xie S, Shu Y, Harasym TO, Harasym NL, Williams L, Bermudes D, Liboiron BD, Saad W, Prud'homme RK, Mayer LD. Modulating the therapeutic activity of nanoparticle delivered paclitaxol by manipulating the hydrophobicity of prodrug conjugates. J Med Chem. 2008;51:3288–3296. - PubMed
-
- Masuda A, Goto Y, Kurosaki Y, Tetsuya A. In vivo application of chitosan to facilitate intestinal acyclovir absorption in rats. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:2449–2456. - PubMed
-
- Larsen A, Holm R, Pedersen ML, Mülletz A. Lipid-based formulations for danazol containing a digestible surfactant, Labrafil M2125CS: in vivo bioavailability and dynamic in vitro lipolysis. Pharm Res. 2008;25:2769–2777. - PubMed
-
- Strickley RG. Solubilizing excipients in oral and injectable formulations. Pharm Res. 2004;21:201–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

