First detection of heartland virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) from field collected arthropods
- PMID: 23878186
- PMCID: PMC3771279
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0209
First detection of heartland virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) from field collected arthropods
Abstract
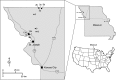
Heartland virus (HRTV), the first pathogenic Phlebovirus (Family: Bunyaviridae) discovered in the United States, was recently described from two Missouri farmers. In 2012, we collected 56,428 ticks representing three species at 12 sites including both patients' farms. Amblyomma americanum and Dermacentor variabilis accounted for nearly all ticks collected. Ten pools composed of deplete nymphs of A. americanum collected at a patient farm and a nearby conservation area were reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction positive, and eight pools yielded viable viruses. Sequence data from the nonstructural protein of the Small segment indicates that tick strains and human strains are very similar, ≥ 97.6% sequence identity. This is the first study to isolate HRTV from field-collected arthropods and to implicate ticks as potential vectors. Amblyomma americanum likely becomes infected by feeding on viremic hosts during the larval stage, and transmission to humans occurs during the spring and early summer when nymphs are abundant and actively host seeking.
Figures

References
-
- Elliott RM. Bunyaviruses: general features. In: Mahy BW, Van Regenmortel MH, editors. Encyclopedia of Virology. Third edition. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier; 2008. pp. 390–399.
-
- Schmaljohn CS, Nichol ST. Bunyaviridae. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. Fifth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2007. pp. 1741–1789.
-
- McMullan LK, Folk SM, Kelly AJ, MacNeil A, Goldsmith CS, Metcalfe MG, Batten BC, Albariño CG, Zaki SR, Rollin PE, Nicholson WL, Nichol ST. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:834–841. - PubMed
-
- Xu B, Liu L, Huang X, Ma H, Zhang Y, Du Y, Wang P, Tang X, Wang H, Kang K, Zhang S, Zhao G, Wu W, Yang Y, Chen H, Mu F, Chen W. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002369. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Zhang L, Zhang QF, Popov VL, Li C, Qu J, Li Q, Zhang YP, Hai R, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhan FX, Wang XJ, Kan B, Wang SW, Wan KL, Jing HQ, Lu JX, Yin WW, Zhou H, Guan XH, Liu JF, Bi ZQ, Liu GH, Ren J, Wang H, Zhao Z, Song JD, He JR, Wan T, Zhang JS, Fu XP, Sun LN, Dong XP, Feng ZJ, Yang WZ, Hong T, Zhang Y, Walker DH, Wang Y, Li DX. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1523–1532. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

