Synthesizing cognition in neuromorphic electronic systems
- PMID: 23878215
- PMCID: PMC3773754
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1212083110
Synthesizing cognition in neuromorphic electronic systems
Abstract
The quest to implement intelligent processing in electronic neuromorphic systems lacks methods for achieving reliable behavioral dynamics on substrates of inherently imprecise and noisy neurons. Here we report a solution to this problem that involves first mapping an unreliable hardware layer of spiking silicon neurons into an abstract computational layer composed of generic reliable subnetworks of model neurons and then composing the target behavioral dynamics as a "soft state machine" running on these reliable subnets. In the first step, the neural networks of the abstract layer are realized on the hardware substrate by mapping the neuron circuit bias voltages to the model parameters. This mapping is obtained by an automatic method in which the electronic circuit biases are calibrated against the model parameters by a series of population activity measurements. The abstract computational layer is formed by configuring neural networks as generic soft winner-take-all subnetworks that provide reliable processing by virtue of their active gain, signal restoration, and multistability. The necessary states and transitions of the desired high-level behavior are then easily embedded in the computational layer by introducing only sparse connections between some neurons of the various subnets. We demonstrate this synthesis method for a neuromorphic sensory agent that performs real-time context-dependent classification of motion patterns observed by a silicon retina.
Keywords: analog very large-scale integration; artificial neural systems; decision making; sensorimotor; working memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

 , which compete against other populations via an inhibitory population.
, which compete against other populations via an inhibitory population.
 on the upper right corner of the screen for
on the upper right corner of the screen for  (red) indicates that the subject must attend to the horizontal bar (indicated by a circle) and report with output A if it enters the right half of the screen. If the initial cue appears on the upper left corner (blue), then the task is inverted: The subject must attend to the vertical bar and report B if the attended bar enters the left half of the screen. The experimental stimuli were presented as black bars against a light background (colors here are used only for the sake of clarity). The agent must respond as soon as the screen midline is judged to be crossed: this fuzzy condition results in different response latencies.
(red) indicates that the subject must attend to the horizontal bar (indicated by a circle) and report with output A if it enters the right half of the screen. If the initial cue appears on the upper left corner (blue), then the task is inverted: The subject must attend to the vertical bar and report B if the attended bar enters the left half of the screen. The experimental stimuli were presented as black bars against a light background (colors here are used only for the sake of clarity). The agent must respond as soon as the screen midline is judged to be crossed: this fuzzy condition results in different response latencies.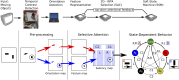
 “silicon retina” (22). The silicon retina output events are preprocessed in software to detect orientation and routed accordingly to one of two possible feature maps, implemented as
“silicon retina” (22). The silicon retina output events are preprocessed in software to detect orientation and routed accordingly to one of two possible feature maps, implemented as  sheets of VLSI I&F neurons. The events produced by the feature maps are retinotopically mapped to a selective attention chip (SAC), which selects the most salient region of the visual field by activating a spiking neuron at that position (black circle in the Saliency map box). The input–output space of the SAC is divided into five distinct functional regions: left (L), right (R), border (X), and cues (C1, C2). The events from each of these regions are routed to the appropriate transition neurons of the SSM. To focus on the desired target, the system must attend to one of the two bars. This is achieved by modulating the attentional layer with a state-dependent top–down attentional feedback from the SSM. In the neural architecture, this is implemented by inhibiting the features corresponding to the bar that should not be attended to (Materials and Methods). Transitions that do not change the state are omitted in the “State-Dependent Behavior” diagram, to avoid clutter. The snapshots shown in the “Pre-processing” and “Selective Attention” diagrams represent experimental data, measured during the experiment of Fig. 4, in the period when the state B0 was active. An additional sWTA network (not displayed) is stimulated by the transition populations to suppress noise and to produce output A or B.
sheets of VLSI I&F neurons. The events produced by the feature maps are retinotopically mapped to a selective attention chip (SAC), which selects the most salient region of the visual field by activating a spiking neuron at that position (black circle in the Saliency map box). The input–output space of the SAC is divided into five distinct functional regions: left (L), right (R), border (X), and cues (C1, C2). The events from each of these regions are routed to the appropriate transition neurons of the SSM. To focus on the desired target, the system must attend to one of the two bars. This is achieved by modulating the attentional layer with a state-dependent top–down attentional feedback from the SSM. In the neural architecture, this is implemented by inhibiting the features corresponding to the bar that should not be attended to (Materials and Methods). Transitions that do not change the state are omitted in the “State-Dependent Behavior” diagram, to avoid clutter. The snapshots shown in the “Pre-processing” and “Selective Attention” diagrams represent experimental data, measured during the experiment of Fig. 4, in the period when the state B0 was active. An additional sWTA network (not displayed) is stimulated by the transition populations to suppress noise and to produce output A or B.

 .
.Comment in
-
Reverse engineering the cognitive brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Sep 24;110(39):15512-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313114110. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24029019 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mead CA. Analog VLSI and Neural Systems. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley; 1989.
-
- von Neumann J. The Computer and the Brain. New Haven, CT: Yale Univ Press; 1958.
-
- Sarpeshkar R. Analog versus digital: Extrapolating from electronics to neurobiology. Neural Comput. 1998;10(7):1601–1638. - PubMed
-
- Seo J, et al. (2011) A 45nm cmos neuromorphic chip with a scalable architecture for learning in networks of spiking neurons. Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC) (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, New York), pp 1–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

