Chromatin insulator bodies are nuclear structures that form in response to osmotic stress and cell death
- PMID: 23878275
- PMCID: PMC3718971
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201304181
Chromatin insulator bodies are nuclear structures that form in response to osmotic stress and cell death
Abstract
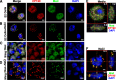
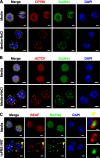
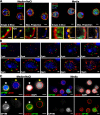
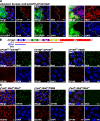
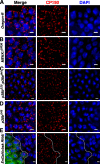
Chromatin insulators assist in the formation of higher-order chromatin structures by mediating long-range contacts between distant genomic sites. It has been suggested that insulators accomplish this task by forming dense nuclear foci termed insulator bodies that result from the coalescence of multiple protein-bound insulators. However, these structures remain poorly understood, particularly the mechanisms triggering body formation and their role in nuclear function. In this paper, we show that insulator proteins undergo a dramatic and dynamic spatial reorganization into insulator bodies during osmostress and cell death in a high osmolarity glycerol-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent manner, leading to a large reduction in DNA-bound insulator proteins that rapidly repopulate chromatin as the bodies disassemble upon return to isotonicity. These bodies occupy distinct nuclear territories and contain a defined structural arrangement of insulator proteins. Our findings suggest insulator bodies are novel nuclear stress foci that can be used as a proxy to monitor the chromatin-bound state of insulator proteins and provide new insights into the effects of osmostress on nuclear and genome organization.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Visualization of chromatin domains created by the gypsy insulator of Drosophila.J Cell Biol. 2003 Aug 18;162(4):565-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200305013. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12925706 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated histone variant γH2Av is associated with chromatin insulators in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2022 Oct 5;18(10):e1010396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010396. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36197938 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Roles of Chromatin Insulator Proteins in Control of the Drosophila Bithorax Complex.Genetics. 2016 Feb;202(2):601-17. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.179309. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26715665 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin insulators: a role in nuclear organization and gene expression.Adv Cancer Res. 2011;110:43-76. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386469-7.00003-7. Adv Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21704228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulators are fundamental components of the eukaryotic genomes.Heredity (Edinb). 2005 Jun;94(6):571-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800669. Heredity (Edinb). 2005. PMID: 15815711 Review.
Cited by
-
When Phased without Water: Biophysics of Cellular Desiccation, from Biomolecules to Condensates.Chem Rev. 2023 Jul 26;123(14):9010-9035. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00659. Epub 2023 May 3. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37132487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The insulator protein Suppressor of Hairy wing is required for proper ring canal development during oogenesis in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2015 Jul 1;403(1):57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.03.024. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25882370 Free PMC article.
-
Subnuclear distribution of proteins: Links with genome architecture.Nucleus. 2018 Jan 1;9(1):42-55. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2017.1361578. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Nucleus. 2018. PMID: 28910577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome compartmentalization: causes, changes, consequences, and conundrums.Trends Cell Biol. 2024 Sep;34(9):707-727. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2024.01.009. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Trends Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38395734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EAST Organizes Drosophila Insulator Proteins in the Interchromosomal Nuclear Compartment and Modulates CP190 Binding to Chromatin.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 21;10(10):e0140991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140991. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26489095 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

